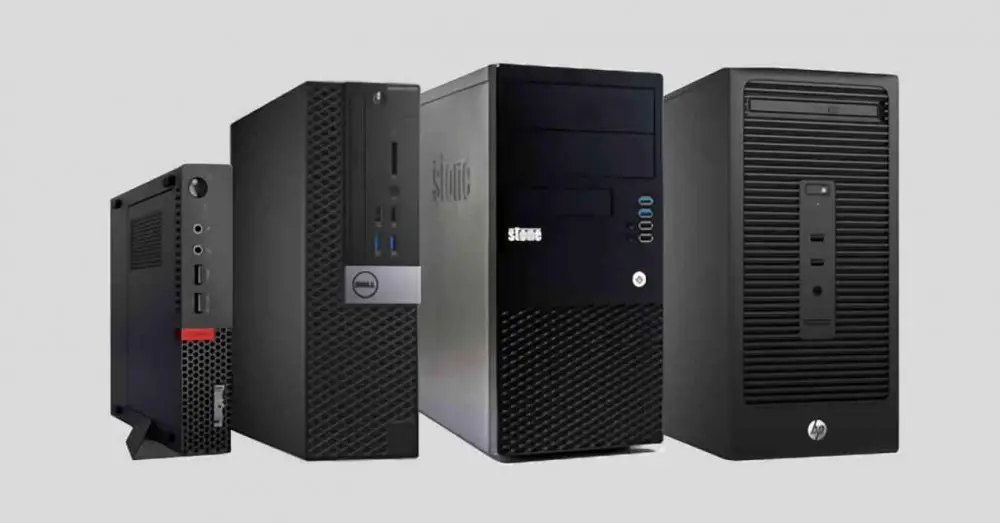

The enormous versatility in terms of PC hardware allows not only a large number of variations in terms of its internal configuration, but also to these variations the different form factors that are in the market must be added. In this article we are going to make a summary of the different form factors.
If you are looking to buy a new PC, it is possible that the conventional tower exceeds your needs or on the contrary, that a more compact system does not give you enough performance for what you need. In any case, there are different form factors that follow a series of standards in terms of size.
In this article we are going to discuss several form factors, both in terms of desktop computers. So that you have a better idea of the type of PC that best suits your needs when buying a new computer.
What do we mean by form factor?

A form factor is nothing more than a generic design from which others are derived. When we talk about form factor in the case of a computer, we are really talking about the size of the box in which the components will go. Which will influence not only the thermal capacities, but also the consumption as far as the internal components of the PC are concerned. We must not forget that the processing power of the processors as well as the bandwidth of a processor have a great impact in the form of energy consumed and heat released.
Not all users have the same needs, this has meant that in recent years new designs of laptops and desktops have appeared for different types of users in the market. All of them with a series of common characteristics that depend on the type of motherboard used in the PC.
The most widely used form factor: the traditional tower or ATX

The first of the form factors is the traditional tower of a lifetime, or known as the ATX form factor. Which has been with us since the days of Windows 95, and if it has already rained more than twenty years.
The ATX towers, due to their expandability and their different size variants, are the quintessential PC and what we refer to as desktop PCs. The different ATX form factors house motherboards with lots of expansion ports and the ability to house high-power power supplies and complex cooling systems. Within the ATX format there are different form factors, whose specifications are as follows:
- ATX: These are towers whose motherboards measure 305 x 244 mm, although there are companies that have launched somewhat larger towers. It is the most widely used type of PC tower today.
- Micro-ATX : A more compact variant of the ATX and with a volume that is 25% smaller, where its motherboards measure 244 mm x 244 mm. Which leads them to support smaller power supplies and have fewer expansion sockets. In 1999 Intel proposed an improved version of itself known as FlexATX, with a size of 229 mm x 191 mm.
- Mini-ATX: With a size per tower of 150 x 150 mm, Mini-ATX towers are much more limited in power consumption and expansion space. That is why computers that are mounted with this type of tower usually include hardware for laptops as a standard.
History and development of ITX formats

In the 90s there was a third company that made x86 CPUs that has been forgotten by many people, its name was Cyrix and in 1999 it had already been acquired by VIA Technologies after buying it from National Semiconductors.
However, Cyrix did not have the muscle or the development capacity of his rivals Intel and AMD. That is why they decided to take completely different paths and a few weeks after buying Cyrix in VIA they decided to acquire Centaur, a company specialized in component integration, which allowed them to launch motherboards with fewer electronic components than the classic MicroATX, to which christened ITX.

Unfortunately, the existence of the MicroATX formats and its Intel variant, FlexATX, caused ITX to not be accepted by motherboard manufacturers, which led VIA to create the Mini-ITX motherboard format. This format was initially devised for office computers designed to function as terminals for a more powerful server and for the creation of set-top boxes to be placed under the television, with this form factor the HTPCs were born.
The development of the Mini-ITX format was initially thought around VIA’s low-consumption processors, which do not require the energy power of the different types of ATX towers, but without losing the expansion capacity, since some mini-ITX units allow you to install small graphics cards.
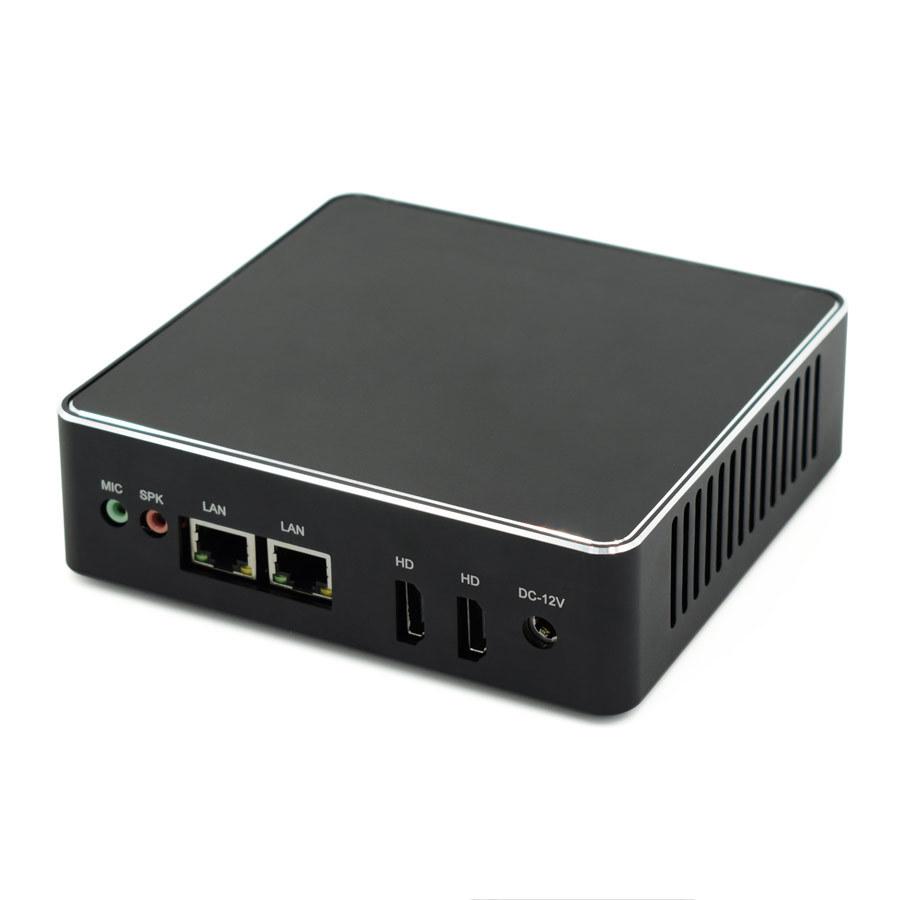

Regarding its size, the Mini-ITX has an even smaller form factor that is the Nano-ITX, which consists of the use of base plates of 120 x 120 m in size and which also allows the mounting of a computer in the car, but the entry of the Intel NUC form factor with smaller motherboards a few years ago has caused the number of Nano-ITX PCs on the market to decline.
PCs integrated into one screen
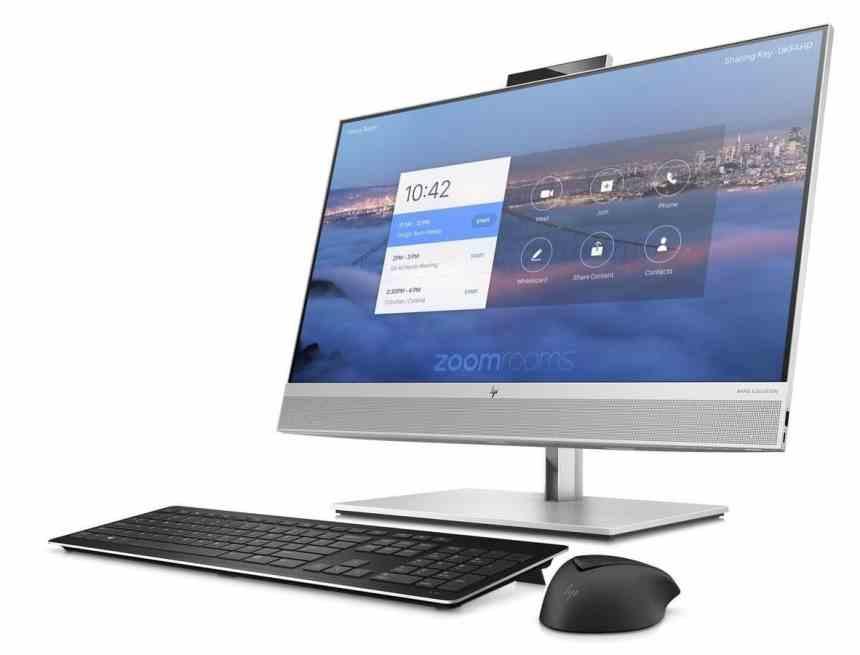
The third form factor, although it is not defined by any type of motherboard in particular are the so-called AiO PCs, they originate from the different Apple iMac models and consist of desktop PCs where everything is integrated into the screen, for example. which do not have the expansion capabilities of the ATX, but take up much less space than a conventional tower.
Its hardware for reasons of space and energy consumption obviously laptop, so they tend to be much more expensive on average than ATX PCs. Do not forget that components for laptops tend to be much more expensive than those for desktop computers. So if you are looking to build a gaming PC we do not recommend opting for this type of form factor even if it comes with a decent dedicated GPU. At the end of the day you will end up paying dearly for the inability to expand and these PCs are not portable either.
Because they are not the best of both worlds, their popularity is not very high among users and fewer and fewer computers are launched under this form factor, since it is much better to buy a tower and then expand its hardware little by little.