Windows offers a range of lesser-known but valuable internal functions and settings. Microsoft‘s commitment to improving security is evident in features like Windows Defender, provided free of charge, and continuous operating system updates. Among these features is Windows 11 kernel isolation, a security enhancement that deserves recognition.
Windows 11 prioritizes security and mandates the use of TPM 2.0, a chip that verifies software signatures, enhancing overall system security. However, kernel isolation, while lesser-known, can significantly bolster your system’s security. Think of it as creating a protective dome over your processor and RAM to improve data integrity.
What is core insulation?
So, what exactly is kernel isolation? It’s a security measure designed to shield Windows processes from malware. It maintains a strict separation between the operating system and peripheral devices through virtualization. Memory integrity, a component of kernel isolation, segregates high-security processes from the rest, creating a virtual barrier between essential and peripheral hardware, ensuring protection against malware.

However, it’s essential to recognize that utilizing this security feature comes at a cost. Much like the security measures you take to enter your house, core isolation involves access control and validation, consuming time and resulting in a performance loss. This feature is primarily intended for professional environments or educational institutions, where rigorous scrutiny of any connecting devices is necessary to maintain system and network integrity.
Activating core isolation in Windows 11 is a straightforward process:
- Press Windows + I or click the Settings gear in the Windows menu.
- Navigate to Privacy and Security > Windows Security.
- Click Open Windows Security.
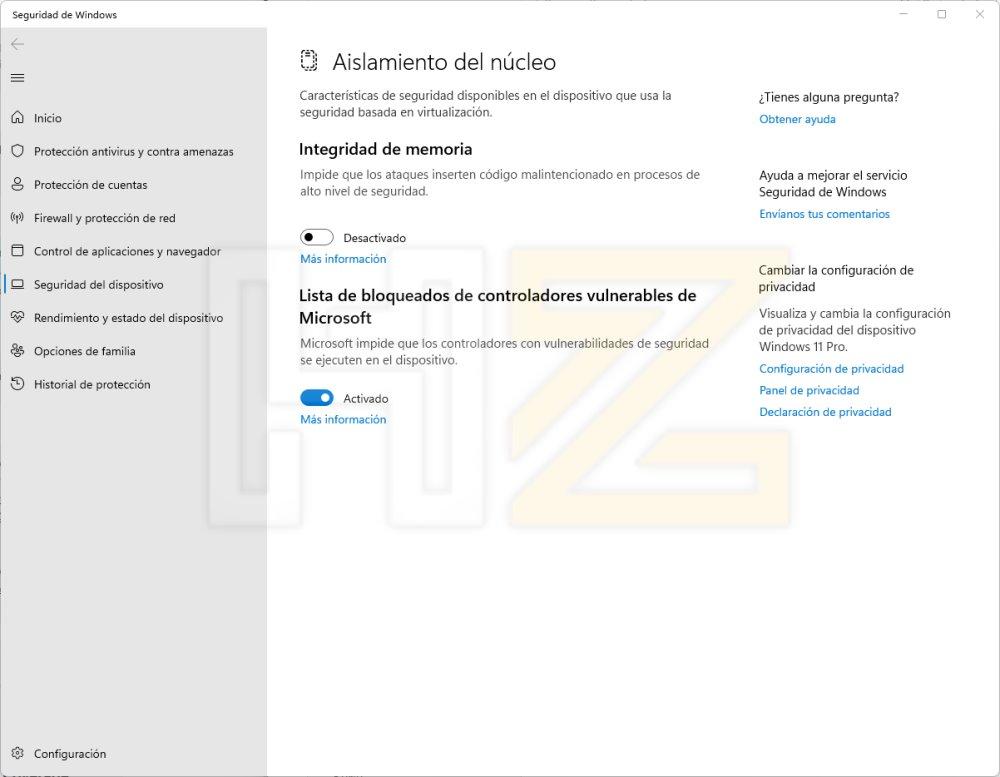
- In the left menu, select Device Security.
- Click Details next to Core Isolation.
- Activate the Memory Integrity option.
- Close the window.
You can enable and disable core isolation as needed, making it useful, especially when connecting potentially suspicious USB devices. While not foolproof, it significantly enhances security.
For Windows 10 users, the process is similar:
- Press Windows + I or click the Settings gear in the Windows menu.
- Go to Updates and Security > Windows Security.
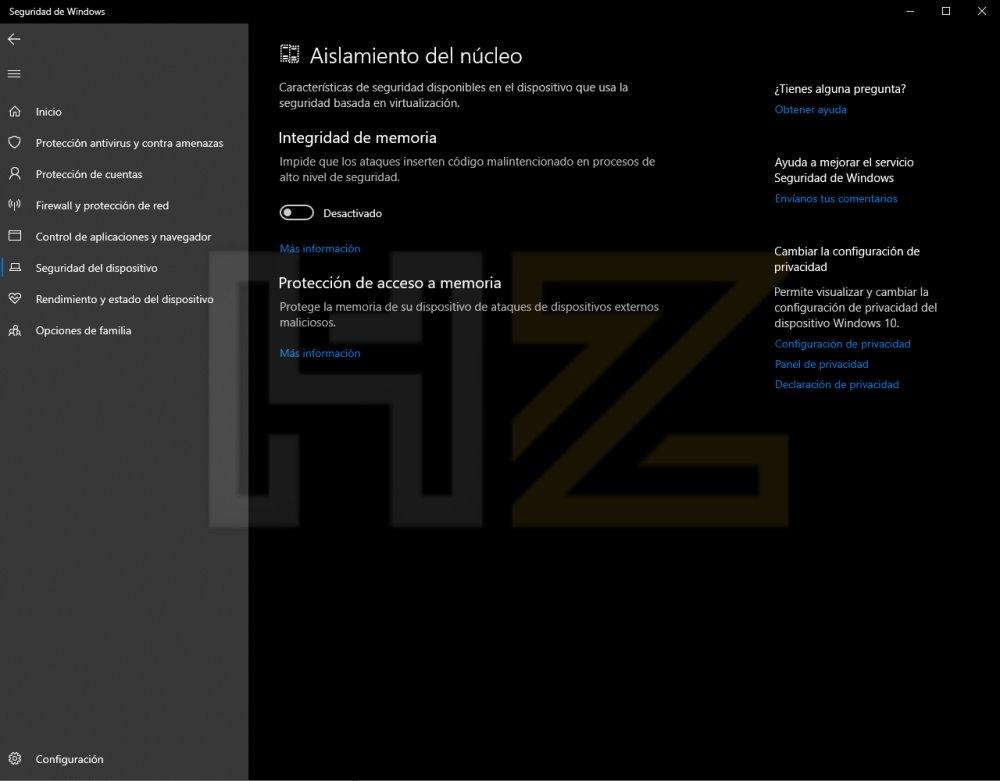
- Click Device Security.
- Click Details next to Core Isolation.
- Activate or deactivate Memory Integrity.
In Windows 10, you can follow the same process multiple times. Enabling this feature can be advantageous when using unknown or untrusted external storage devices, offering an extra layer of security.
In conclusion, kernel isolation is a valuable addition for office or educational settings and when connecting unfamiliar USB drives. It’s an effective measure to mitigate the risk of malware, especially from external storage devices. However, for regular use, it’s recommended to disable this feature as it may have a minimal impact on gaming performance.