As you well know, the power supply is one of the most important hardware components of the PC , since as we always say it represents the heart of the PC since the proper functioning of the rest depends on this component and, in fact, if the source it doesn’t work nothing works. In this article we are going to tell you what the power supply is , how it works, what characteristics it has and what type of power supplies we can find.
Faced with the question of what a power supply is, I am sure that the vast majority of you will say that it is that component that the current is connected to and that is responsible for supplying energy to everything else, and indeed you are right although a bit basic level. For this reason, we are going to go into detail to tell you in depth not only what it is, but how this vital component works.

What is a power supply and how does it work
As we have already mentioned, the source is the one in charge of supplying the energy to the rest of the PC components. But, first of all, you must understand that there is a vital difference in terms of electrical supply and that it could not be carried out if the source does not do its job, and that is that the energy that comes to us from the electrical outlet of the plug is alternating current And yet the PC parts run on direct current. Therefore, one of the sub components that make up the power supply is the AC / DC converter (yes, like the heavy metal band), which literally converts alternating current into direct current so that the PC can use it.
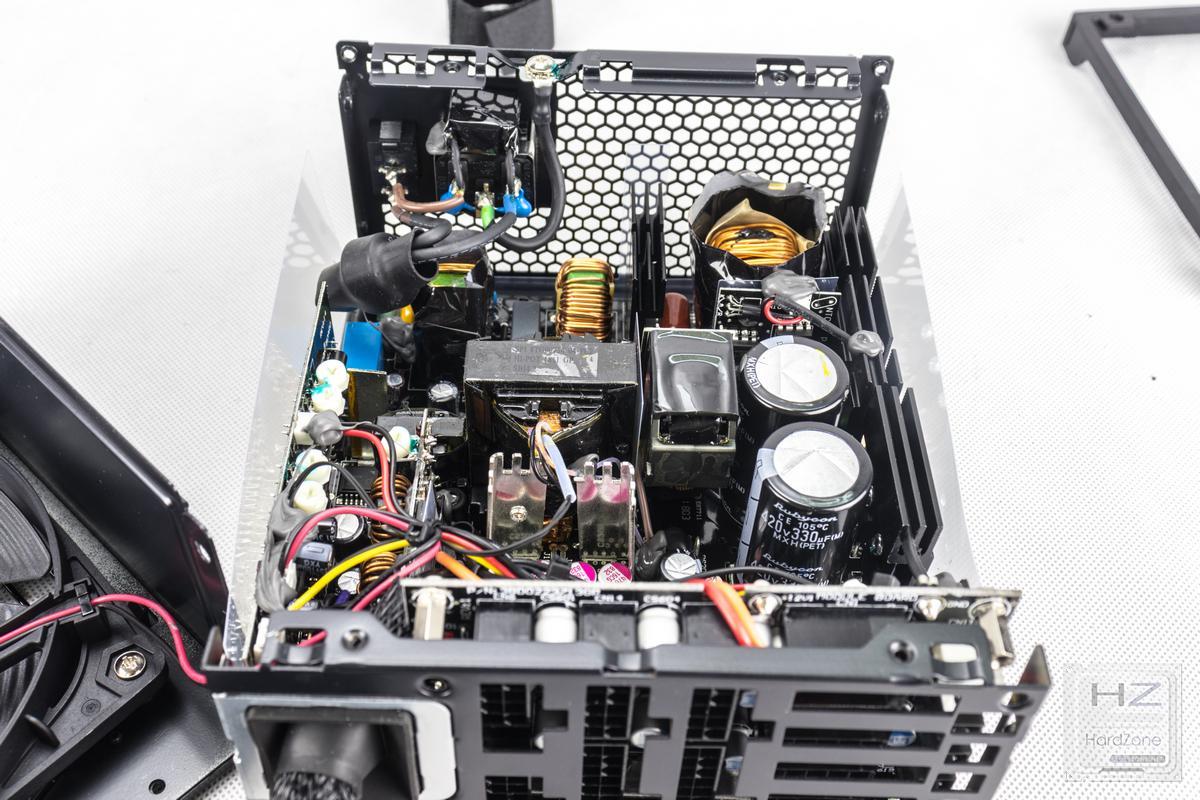

But the thing does not stop there; In addition to converting alternating current into direct current, the source needs to be able to supply the PC components with the exact voltage they need, and as many of you will know, there are mainly three values that are needed: + 12V, + 5V and +3 ,3 V. Therefore, internally the power supplies also have voltage converters to be able to give each component exactly the voltage that it needs, neither more nor less.
In addition to this, all power supplies have filters (these are the Y and X capacitors that we can find both in the input socket and in different components) that are responsible for ensuring that the current is supplied without electrical noise, which we usually call it “clean stream”. The quality of these filters depends on the fluctuation of the current that is supplied, and they bear a large part of responsibility in terms of efficiency and protection systems.
How does the power supply work?
As we have already mentioned, the first function of the power supply is to convert the current from alternating to direct, and that is done with the AC / DC converter. In the past, this same converter had three outputs (for voltages of 12, 5 and 3.3 volts) but that was quite inefficient and also generated a lot of heat, so modern sources convert all the voltage that enters them to + 12VDC, and then through three independent DC / DC converters they generate the voltages of +12, +5 and + 3.3V. This is done because the least used voltages (5 and 3.3) are not converted if they are not used, saving a lot of energy and heat.

Once we have the voltage we need, it is filtered using inductors and capacitors, and here two more parameters come into play: voltage regulation to ensure that the voltage is stable and electrical noise , since the higher the noise, the more the cables wear out. components due to heat. We will explain this.
PC power supplies use a switching technology to convert alternating current to direct current; While the rectifier is on or off, direct current pulses are generated at a rate established by the alternating current input (which, in the case of Spain, is 50 Hz, but in Mexico, for example, it is 60 Hz). These pulses generate noise.
The current of each voltage passes through an inductor (called chokes) that stabilize and smooth the wave frequency of these pulses, reducing noise. Then it goes to the capacitors (the famous Japanese capacitors come into play here), which store the electrical charge and release it again without the noise we’ve talked about. The way to do it this way is because if the voltage entering the capacitor raises or lowers the switching frequency, the charge of the capacitor goes down or rises but in a much slower way than the switching frequency, while the output of the capacitor is always fixed, without variations, or as we have said before, “clean”.
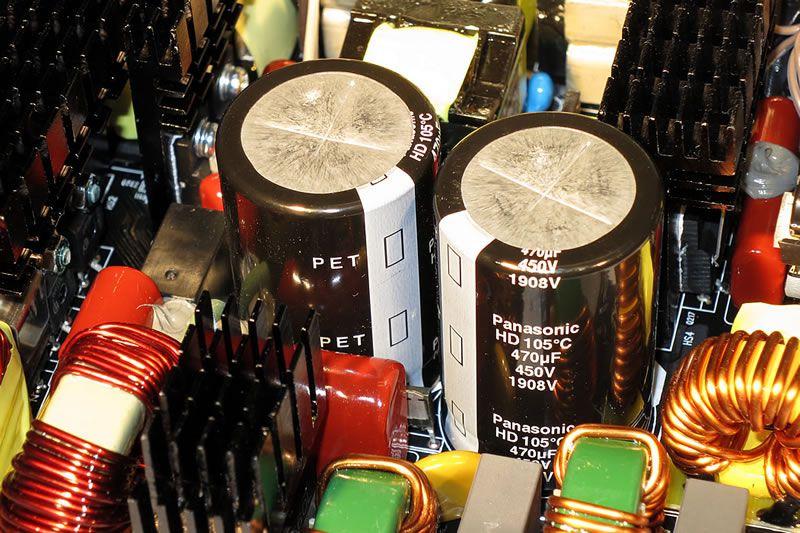

Obviously it is almost impossible to get a perfectly smooth graph in terms of the output voltage, since even though we have eliminated almost all the noise, waves (Ripple), small peaks and valleys in the output voltage are created. This is where large, series-arranged capacitors come into play again, as the slower the change between the highest and lowest voltage, the more stable the output voltage.
Some of you may wonder why many more capacitors are not inserted then, and the answer is because it would reduce the efficiency. No electronic component is 100% efficient and a small part of the energy is always transformed into heat. In the case of condensers, almost all the heat they generate is precisely due to the electrical noise they eliminate, but even so this is the reason why we will normally see that the sources have two of these famous large capacitors and no more. We must find a balance.
Let’s take an example: in the following image you can see the Ripple from a source that does not have good filtering, or in other words, its capacitors are not of good quality.
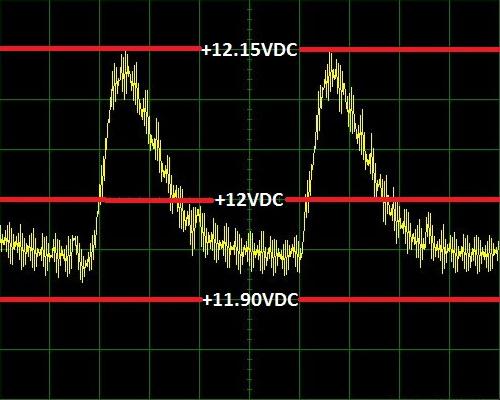
Now, in this other image you can see the + 12V output of a high quality power supply.
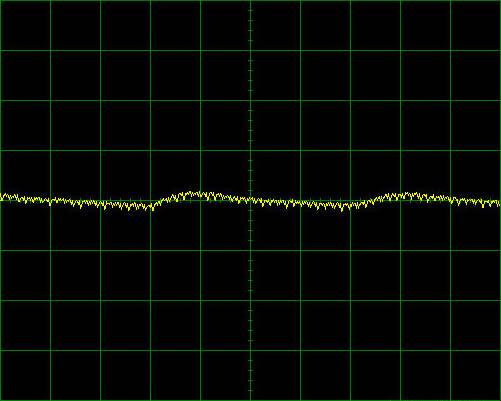
After all these leaks, there is still a lot of work to do before the power goes out to the rest of the PC components. As we mentioned before, the voltage regulator has a very important responsibility since it is the one in charge of determining how well or badly the source responds to sudden load changes (or consumption), such as when we start a benchmark.
This is where Ohm’s famous law comes into play, which defines that the more the current intensity (Amps) increases, the more the resistance increases, and the more resistance, the more the voltage rises (the resistance is the only value that remains unchanged since it depends of the physical components). A good quality source must be able to compensate for all this, usually by internal monitoring performed by the “supervisor IC”, capable of telling the source’s PWM controller that the rectifier needs to switch to a different frequency to adjust the voltage. output.
In this regard, digital power supplies are vastly more effective than normal ones as monitoring is done digitally, making compensation run much faster. The slower this switching is, the more components suffer from heat wear, which also reduces efficiency.

In addition to everything that we have explained so far, we must bear in mind that in reality the PC not only works with three voltage values (12, 5 and 3.3V), but for example the DDR4 RAM uses between 1.2 and 1.35V to run. The voltage regulator is also responsible for this, supplying the voltage that each component needs; for example, in the case of RAM, the voltage is supplied from the + 3.3V rail, since it is the closest.
Types and categories
Power supplies can be categorized by Tiers, but this is an assessment of how well or badly they work, which is subjective after all. However, they can be categorized starting with their efficiency, determined by the 80 Plus certification.
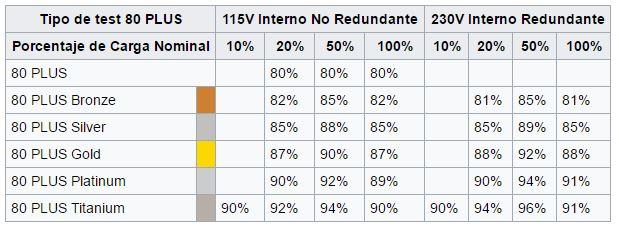
The EEC (European Economic Community) established that the parameters defined by the 80 Plus Bronze certification (whether they have this certification or not) are the minimum for a manufacturer to be able to sell their products in Europe. In any case, this certification is already held by only entry-level power supplies, while the Silver and Gold seals are much more common, and the Platinum and Titanium are already reserved for high-end power supplies.
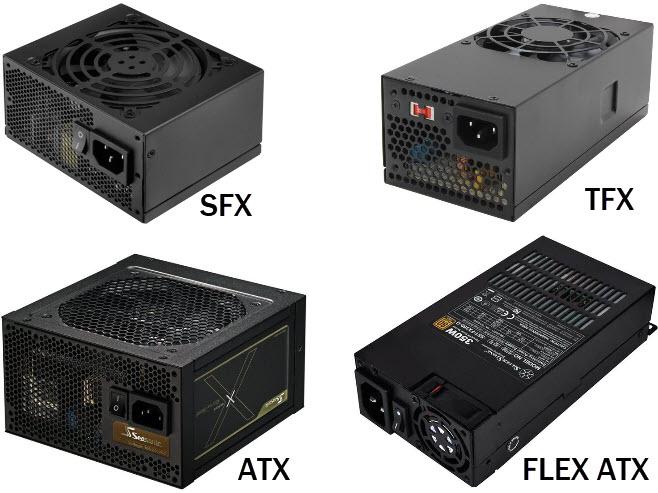
On the other hand, we can also classify a power supply by its size or form factor, since it is defined by a standard:
- ATX : the current standard, with dimensions of 150 x 150 x 86 mm, although they are also ATX sources that have greater length as long as the 86 mm height and 150 mm width are respected.
- SFX : dimensions are smaller as they are designed for small form factor systems. They measure 100 x 125 x 63.5 mm, and require an adapter to be able to install them in standard ATX boxes.
- SFX-L : is a variant of the SFX sources that allow you to install a larger fan. They measure 130 x 125 x 63.5 mm.
- TFX : they have dimensions of 85 x 65 x 185 mm, and are generally thought for special equipment and servers.
- Flex ATX : they are a variant also used in servers and special equipment that has the particularity of allowing hot “plug and play”, that is, in systems with two redundant sources, one can be removed and the other installed without shutting down the system. They measure 150 x 81.5 x 40.5 mm.
