As we store all kinds of files on our PC, the free space on our hard drive is running out. And if we have an SSD, which although they are faster generally tend to have less space, because we will run out of space much sooner. Therefore, if we want to avoid suddenly finding ourselves with a message that tells us that there is no free space and that the hard disk is full , it is necessary to know how to control it and to know which files and folders occupy the most. And so we can do it from Linux.
In Windows, controlling the free space of hard drives and SSDs is quite simple. In Linux, the truth is, it is not much more complicated than in Microsoft‘s operating system, but we must be clear about how it is done. As for most tasks, we can find several ways to do this in Linux, either through a terminal or through applications with a graphical interface .

Check free space in Linux from Terminal
Use the df -h command
The DF command is one of the most basic that we can use in a terminal. This command comes from the name “disk-free”, so its purpose is precisely to show us the free space we have on our hard drives, and mounting points, within any Linux system.
To do this, what we must do is open a terminal and execute the following command in it:
df -h
This command will show us the free space in data that we can read, such as MB and GB.
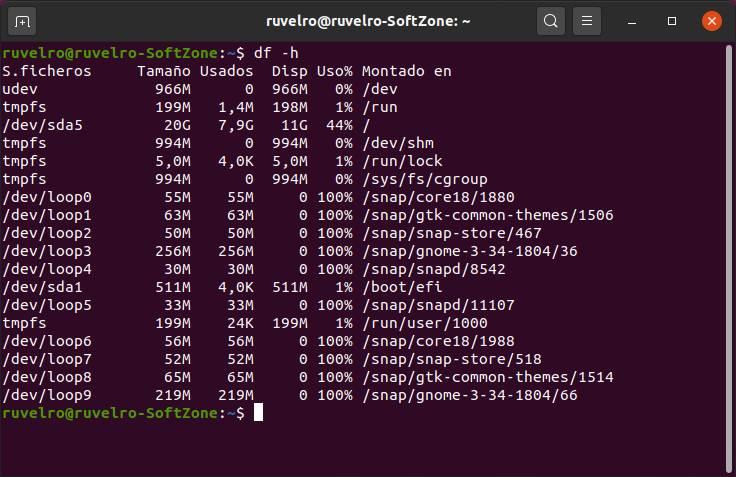
As we can see, this command lists all the mount points of our system, and shows us the information for each one of them. We can see the total size of each mount point, the occupied space and the space that is available. We can also see the percentage of use.
Check the size of each directory with du -h
The du command is a tool, in a way, similar to the previous one. With it we will be able to control the space we have occupied on the disk of our Linux, but in a different way. While df focuses on showing the free space of each mount point, du (disk-usage) shows us the size of each of the directories on our disk.
We can run this tool with:
du -h
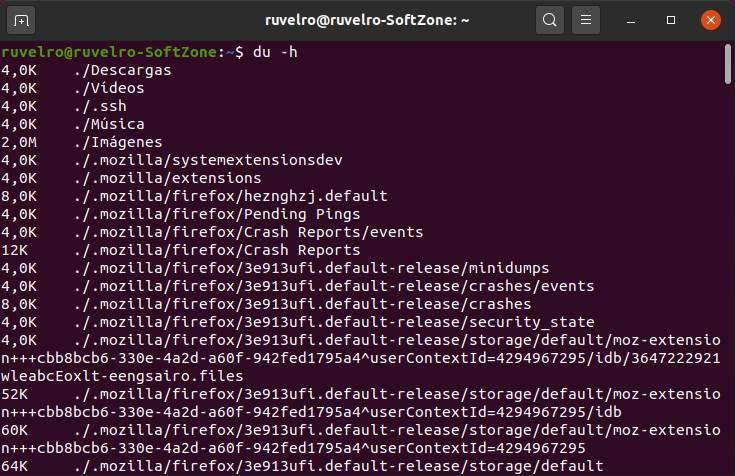
The information comes out all piled up, so then it is our task to go looking for the directories that interest us to see how much they occupy.
NCurses, more complete for terminal
NCurses Disk Usage is a complete disk analyzer that runs from the terminal, but has its own interface. This tool will allow us to see all the directories on our hard drive and the size that each one occupies. In addition, we can navigate through the directory tree to see the size of the subfolders and even go as far as seeing the list of the files that occupy the most.
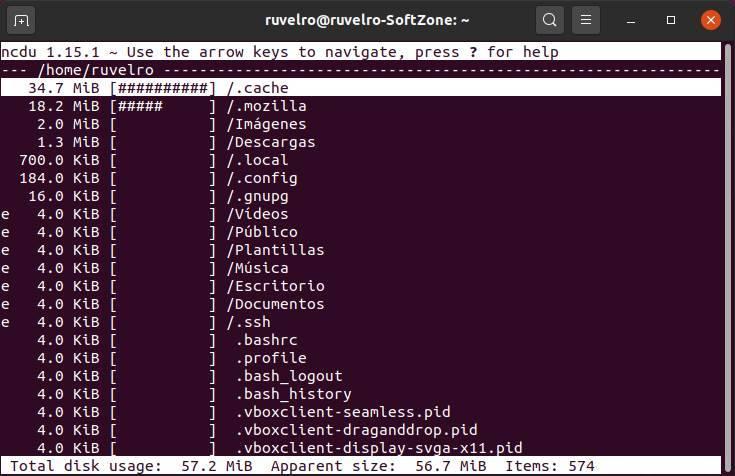
With ncdu we will be able to move through all the directories, and even delete those files, or folders, that occupy the most space. It is not as simple or intuitive as other programs, but it is undoubtedly one of the most complete for those who like to use the terminal for everything.
We must download it by hand from here (there is a compiled version that we do not have to compile ourselves) and run it.
Programs to control the available space on the hard disk
Disk analyzer
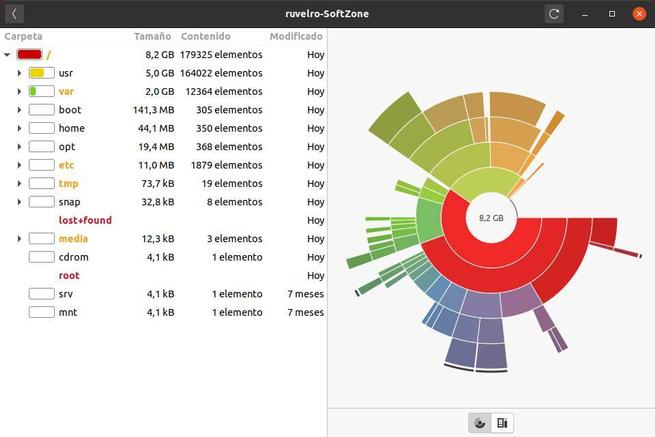
One of the tools with a graphical interface that we can find for Linux is the disk analyzer . This tool is part of the GNOME desktop, so we can find it installed by default on any distro that uses this desktop, such as Ubuntu.
This tool will show us all the units connected to the PC, and we will be able to graphically see the occupied and free space of all of them.
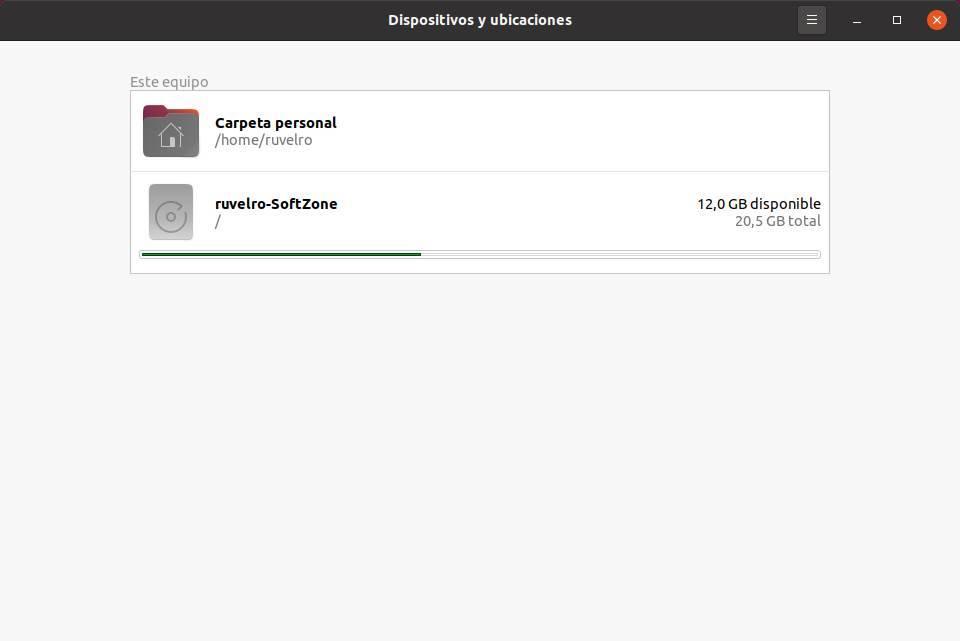
If you want to see this information in more detail, you can click on any of the units to analyze it. So we will be able to see which directories are the ones that occupy the most space on our hard drive. This analyzer will show us a directory tree in the form of a graph and we will be able to see very clearly how much space each of the branches of the directory tree occupies.
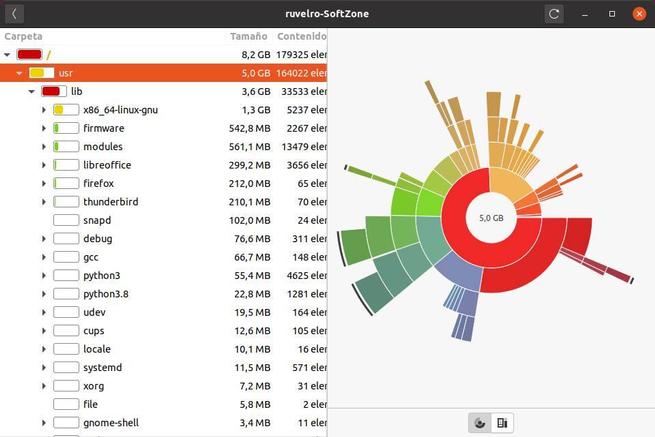
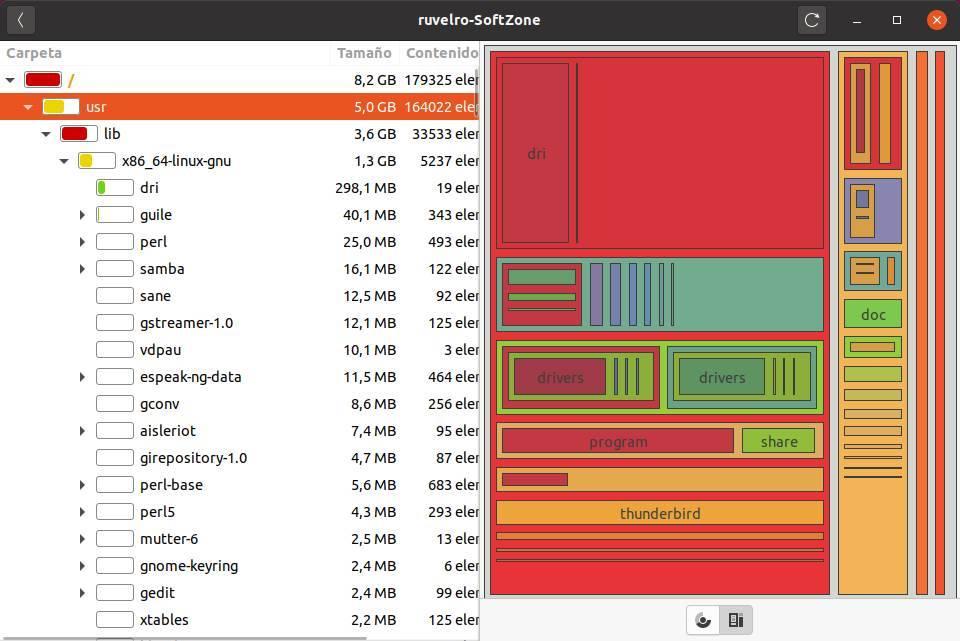
We can even dig deeper into each directory to see it in more detail.
GNOME Disk Utility
Another way to see free space on hard drives, much simpler than the previous one, is to use the GNOME desktop disk utility. This utility is primarily intended to work quickly with partitions, format drives, and mount and unmount disks. But it is also a very fast way to know how much space we have occupied and available, although less detailed than the previous one.
We will look for “Disks” in the application launcher of the distro and we will be able to see a window like the following one.
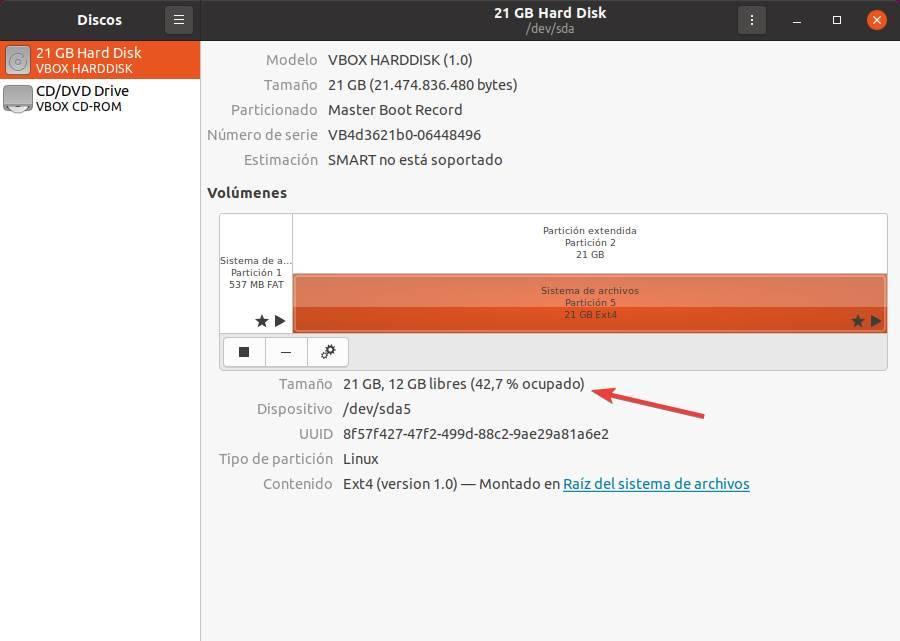
In this window we can see all the partitions in detail, and if we select one of them we can see the space we have occupied and how many gigabytes we have left.
QDirStat, the most complete
QDirStat is the successor to KDirStat, and its development focused on eliminating all KDE dependencies in order to be a completely independent program whose use does not imply installing the entire desktop. This program has a very simple interface within which we will be able to find all the mounting points of our Linux.
We will be able to see how much each directory occupies of each of the mount points. And we will be able to deepen as much as we want in the tree until we reach the files. In the upper part we can see the directories as such, while in the lower part we will find the tree map that will allow us to see, in a much more graphic way, how much each directory and each of the files on the hard disk occupy. We can even delete the folders or files that occupy the most from here.
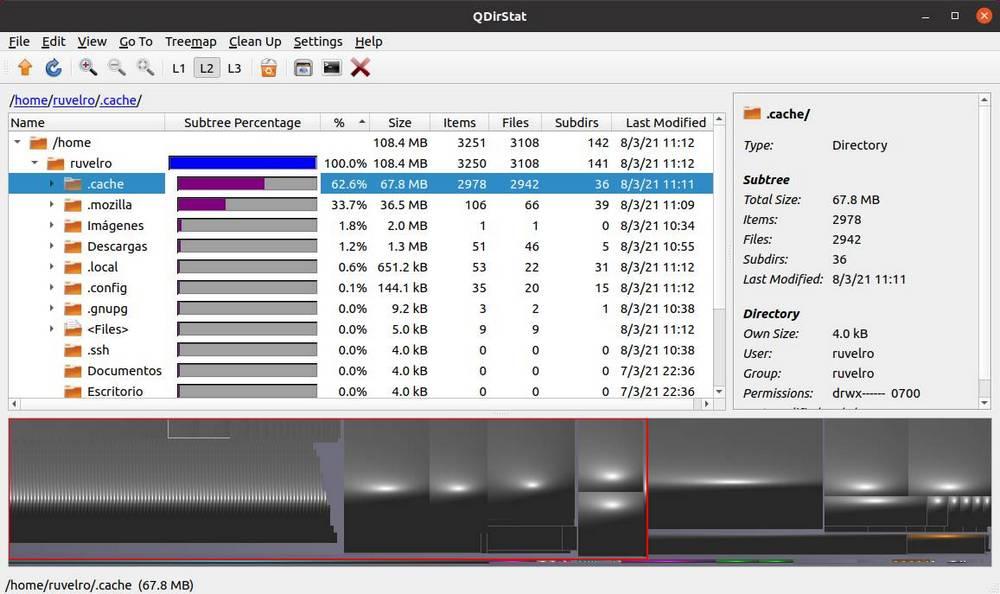
This program is usually included in the main repositories, so to install it we will simply have to run in a terminal:
sudo apt install qdirstat
When the installation of the program is complete, it is ready to start using it.