Today, all motherboards on the market have an integrated network card (so its name has already lost some of its meaning), but it was not always the case. In this article we are going to tell you what a network card is, what features it has , and in case you are also interested a little of its history .
As we said, nowadays it doesn’t make much sense to call a network card “card”, but in reality it has many other names: network card, network adapter, LAN adapter, network interface, or its English terms Network Interface Card or Network Interface Controller (NIC). Whatever you call it, let’s see what it is exactly and what it does.
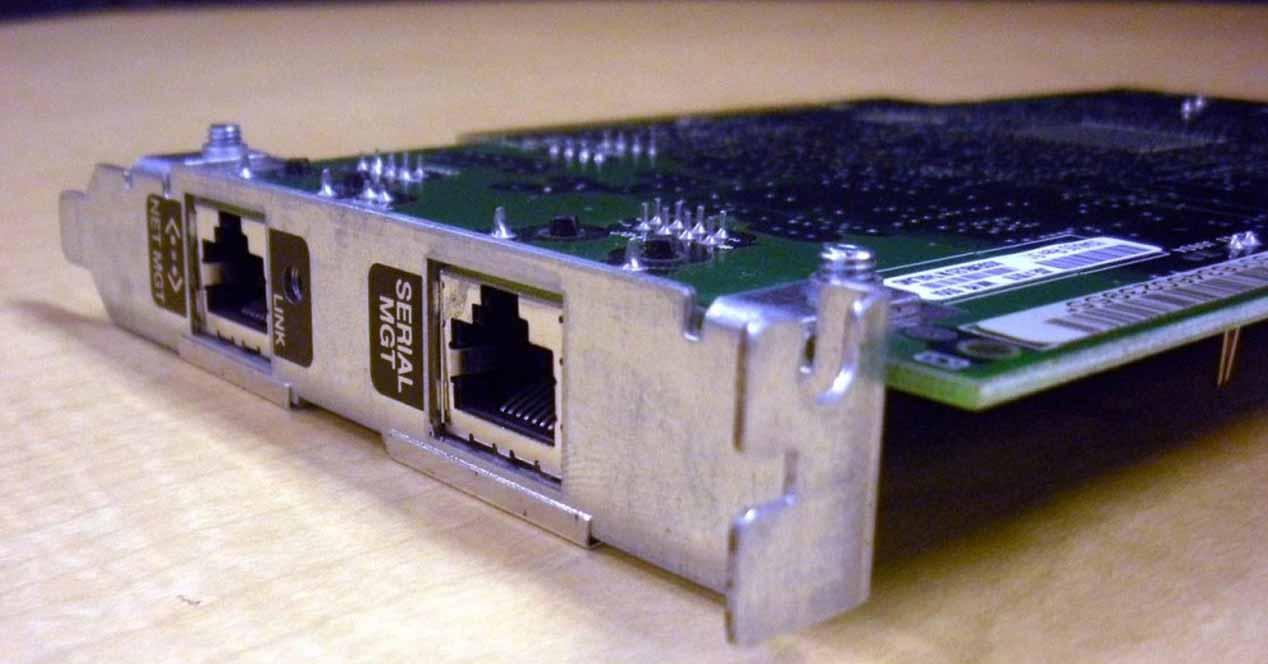
What is a network card?
As you will already suppose, a network card is so called because in the past they were expansion cards that served to provide a desktop PC with network connectivity, adding an RJ-45 port to which to connect a cable and be able to connect to a LAN ( local area network) or WAN (wide area network). In other words, it is what allows you to connect your PC to the Internet .
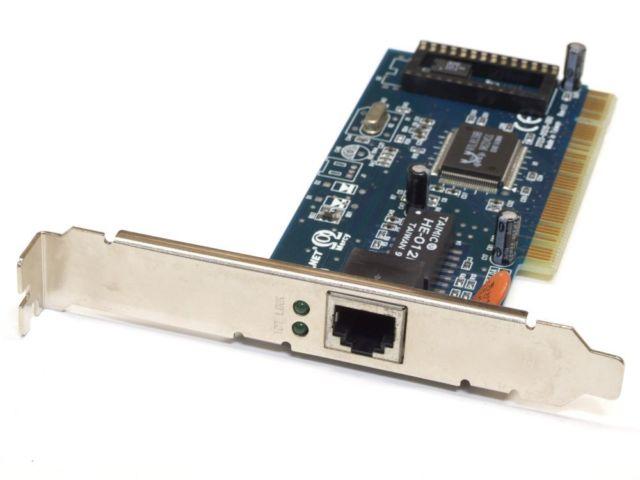

Before these cards were precisely cards, and were connected to the PC through an ISA, AGP and then PCI socket, but since then they began to integrate directly into the motherboards of the equipment, making them unnecessary as an expansion card today. . Nevertheless, they are still used with a PCI-Express interface, although almost all of their market is in the professional environment for servers.
Now the network controller is integrated in the chipset of the motherboard or implemented with a dedicated Ethernet chip as in some high-end motherboards (for example, the famous Killer network cards), with the integrated RJ-45 connector or connectors. on the connectors on the back of the motherboard.

Today all network cards use an RJ-45 type connector , also known as ” socket 8P8C ” where the network cable is connected, but older network cards used BNC or even AUI connections. The vast majority have two status indicator LEDs, the one on the left that when lit shows that a connection is established, and the one on the right – the one that blinks – to show network activity.
Types of network cards
You will already assume that there are at least two types of network cards, right? The ones integrated in the board and the ones that are an expansion card. Well, in reality it is not so, these two belong to the “Ethernet” type because what defines the type of network card is not its form factor, but its architecture .
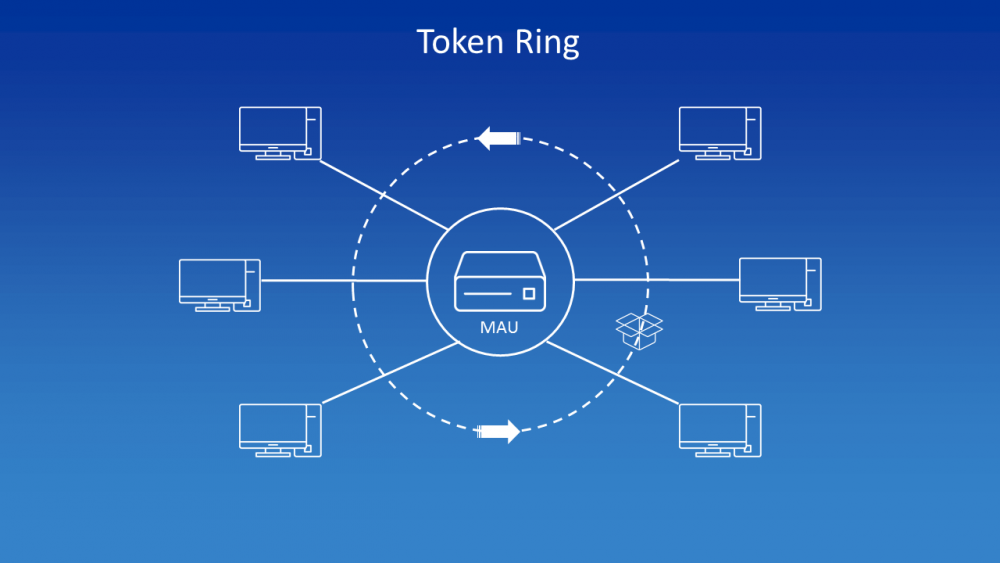
Thus, it all starts with Token Ring network cards, currently no longer in use. It is an architecture designed by IBM in the 70s with a ring-shaped logical topology (hence its name) and with a token access technique using a 3-byte frame called a token, which is the one that travels around the ring. This topology used the IEEE 802.5 standard, but was long ago replaced by the Ethernet standard.
The second type is called ARCNET , which stands for Attached Resource Computer NETwork, a local network architecture that uses the token passing technique as Token Ring, but in this case its topology is star-shaped. Like Token Ring, it is currently deprecated, it used rotary BNC cable, its maximum speed was 2 Mbps and it was a mere local area protocol, with no WAN output.
The third type is Ethernet , which we all know. There are many technologies that this standard uses, so let’s see them:
| Technology | Transmission speed | Type of cable | Maximum distance | Topology |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10Base2 | 10 Mbit / s | Coaxial | 185 m | Bus (T connector) |
| 10BaseT | 10 Mbit / s | Twisted pair | 100 m | Star (Hub or Switch) |
| 10BaseF | 10 Mbit / s | Optical fiber | 2000m | Star (Hub or Switch) |
| 100BaseT4 | 100 Mbit / s | Twisted Pair (category 3UTP) | 100 m | Star. Half Duplex (hub) and Full Duplex (switch) |
| 100BaseTX | 100 Mbit / s | Twisted Pair (category 5UTP) | 100 m | Star. Half Duplex (hub) and Full Duplex (switch) |
| 100BaseFX | 100 Mbit / s | Optical fiber | 2000m | Does not allow the use of hubs |
| 1000BaseT | 1000 Mbit / s | (category 5e or 6UTP) | 100 m | Star. Full Duplex (switch) |
| 1000BaseSX | 1000 Mbit / s | Fiber optic (multimode) | 550 m | Star. Full Duplex (switch) |
| 1000BaseLX | 1000 Mbit / s | Fiber optic (single mode) | 5000 m | Star. Full Duplex (switch) |
As you can see there are many different ones, although the one that is most used currently for the home user is the 100BaseT, also known simply as Gigabit. Currently working with 10GbE and even higher network cards .
Finally, the fourth type of network card out there is WiFi , a technology that allows the wireless interconnection of devices, and this type of connection requires a wireless network access point to be able to work, generally the router. There are WiFi network cards that connect to the PC via USB, but there are also some that connect as an expansion card.