
Surely in recent times you have heard or read about the term Edge Computing, a concept that many media use on a regular basis as something daily but that if no one explains it to you can be a bit difficult to understand. Do not worry, because next we are going to explain what Edge Computing is , what it consists of and what the hardware influences in this regard.
Today there are an infinity of technologies and terms related to them that most people do not fully understand, settling with a basic concept of it to understand, at least, what it is related to. Edge Computing is one of those terms that sounds the most bombastic, since if you know a little English it will make you understand that it is something like “edge computing”, but its meaning really goes far beyond this concept. .
What is Edge Computing?
Edge Computing is a technology designed to define and revolutionize the way we connect to the Internet, meaning the interaction that human beings have with connected devices. It is said that it will affect all industries and sectors, covering sectors ranging from automotive to video games, so as you will understand its importance can be quite broad.
However, to understand how Edge Computing works, it is first necessary to understand other terms such as cloud computing (known as Cloud Computing) or the Internet of Things (IoT), so that you know what happens every time. you turn on your PC or open an Internet browser on your Smartphone.
How Cloud Computing works
Today the cloud is very present everywhere, to the point that you are most likely using it without even realizing it. Every time you upload a file to a service like Google Drive, you know that you are uploading it “to the cloud”, but you are also using it when, for example, you consult your bank’s website to check your financial situation or even when you use one of the many social media. To simplify this concept as much as possible, we can say that every time you interact with data that is on a remote server over the Internet, you are making use of “the cloud”.
The process for all this is as follows: first, your device connects to the Internet and, from there, your ISP (Internet provider) is in charge of handling the data from your device (requests) to the remote servers and then do the reverse. delivering the answers, but going through an internal data processing center in between.
The server or data center processes your data, operates with the information and therefore returns a response. For example, when you connect to email from your device (be it a PC or a smartphone, it doesn’t matter because the data is in the cloud) you are asking the email provider’s server to show you the status of your inbox. email, it processes the request, checks its database if you have new emails and returns the response you see on your screen.
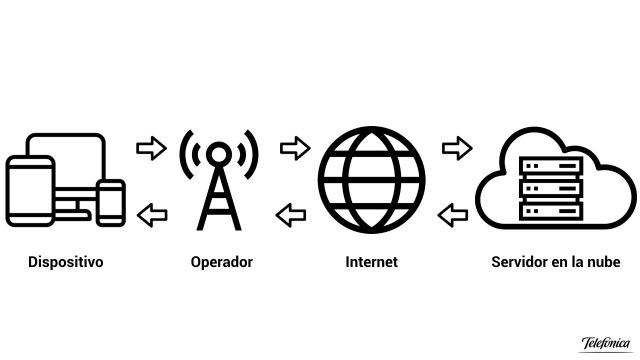
Although this may seem simple, in reality the journey of this information covers a whole series of servers and computers and uses a series of protocols and quite complicated elements, and this carries a series of disadvantages. For example, if you live in Spain and want to check your email but your provider’s server is in the US, every time you connect the information you have to make a long one-way trip, wait for the data to be processed in the provider’s server hardware, and then make the return trip to show you the result, resulting in a long wait time.
Advantages of Edge Computing
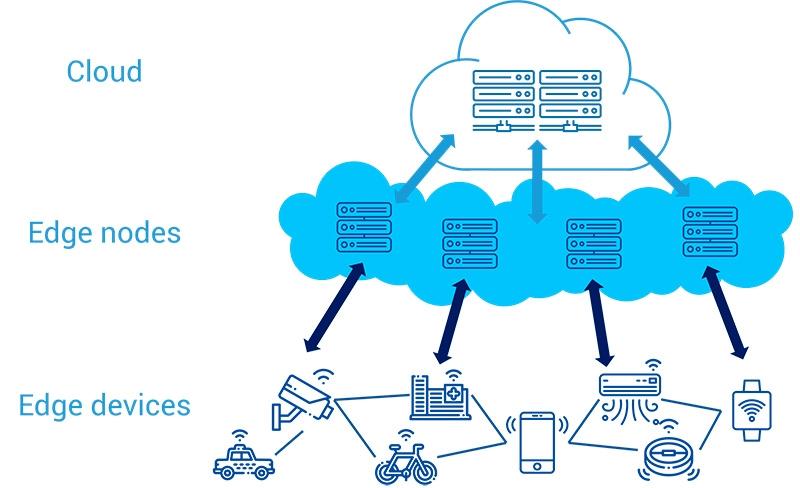
The advantage of Edge Computing with respect to what we have explained so far is that it really consists of, literally, “bringing” the processing power as close as possible to where the data is generated, that is, it consists of bringing the cloud closer to the user to the very edge of the network (that’s why it’s called Edge), so latency is greatly reduced. You can see it quite clearly in the following animated image, courtesy of Telefónica.
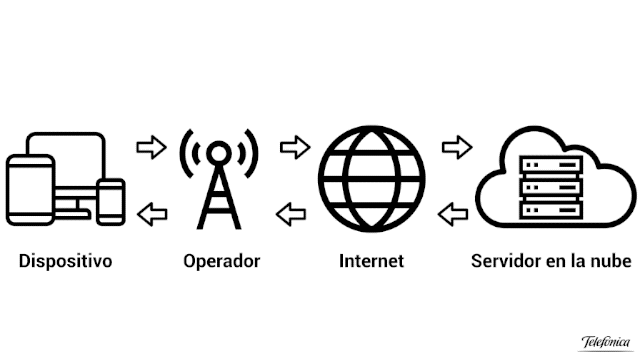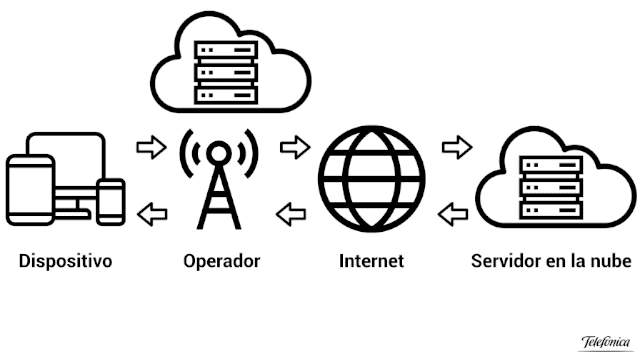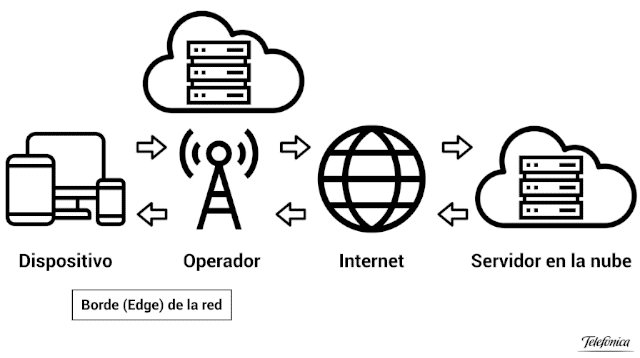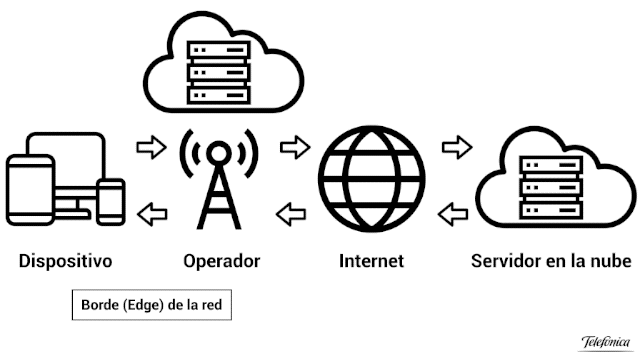
Many of you will wonder, and with good reason, what we can understand by “the edge of the network”. The term depends on many variables, but for example if we are talking about a smartphone, the edge would be the telephone antenna to which you are connected and which is providing you with the Internet service. On the PC you have at home, the edge could be your router without going any further, although the normal thing is that it is the data processing center of your Internet provider.
And this is where the importance of hardware comes into force, because since we are talking about data processing it is where processors become vitally important. Processors, as you well know, have the ability to process and handle data and instructions and, thanks to this, with Edge Computing the capabilities of a data processing server can be virtualized and the possibility of this processing being carried out is enabled. on devices at the edge of the network rather than on distant servers.
This makes it possible to move information and processing capacity that were previously in servers located anywhere on the planet, in a service “in the cloud”, much closer to the user, greatly increasing performance. This represents a huge paradigm shift, since although the functions are similar, as the data processing happens much closer to the user, the speed skyrockets, the latency is reduced and the power is multiplied.
And how does it influence video games?
For some years now, one of the biggest challenges in the video game industry has been being able to offer ways to play anywhere. Since the first GameBoy was presented in 1989 to Google Stadia in 2019, things have changed a lot, and we have gone from a simple portable console with battery that allowed you to play individually to the game in the cloud that allows you to enjoy great video games without having to have a powerful gaming PC.

To make this a reality, of course the power of cloud computing is used, and instead of processing the graphics of the games on your PC, they are processed on powerful remote servers that simply interact with the user and send the resulting images in streaming form. Of course, every time the user presses a button, he has to go through the whole process that we have explained to you before: the information travels to the ISP, its data center, to the server in the cloud, it processes it and then it has to do the whole trip. back, resulting in very high latency.
For the player to perceive that the process from when he presses the button until it takes effect in the game he sees on the screen is instantaneous, the latencies have to be as low as possible and that is where Edge Computing comes in again, approaching the power of that remote server in the cloud at the edge of the network and making the gaming experience much more similar to that if the user were running the game on their PC or console.