Many of Intel‘s security problems on different platforms come through it, especially those implemented as of 2017. It is a key piece in Intel’s architectures from that year and instead, it has been widely attacked by different types of users and groups in order to break their security. We talk about Intel CSME , why is it so important and what exactly is it?
Although few will know it and know of its tremendous possibilities, the Intel CSME has evolved over the course of the few years of life, not without controversy. It is the best weapon that Intel currently has to maintain the confidence and security of each platform and therefore, it does not stop receiving continuous improvements and updates based on firmwares.
Intel CSME, the cornerstone for all the company’s PCH
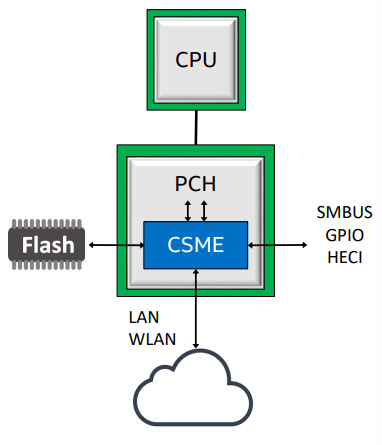
Intel named the successor to MEBx (Management Engine BIOS Extension) from 2017 as CSME, which would be a completely new and much improved version of the first. CSME refers to the acronym of Converged Security & Manageability Engine , something like the security engine and convergent administration capacity of each platform.
Currently it includes three sections / modules much better known than its own term and tremendously relevant to each motherboard such as:
- Management Engine (ME)
- Server Platform Services (SPS)
- Trusted Execution Engine (TXE)
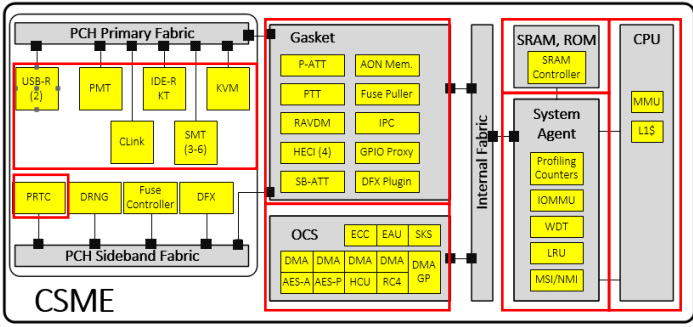
Looking at the sections it is clear that CSME is the root of the trust of each Intel platform. Its main function, broadly speaking, is to provide an isolated and protected execution environment from the host as software that runs directly on the CPU using firmware that is completely transparent to the CPU.
Three main roles that determine its use
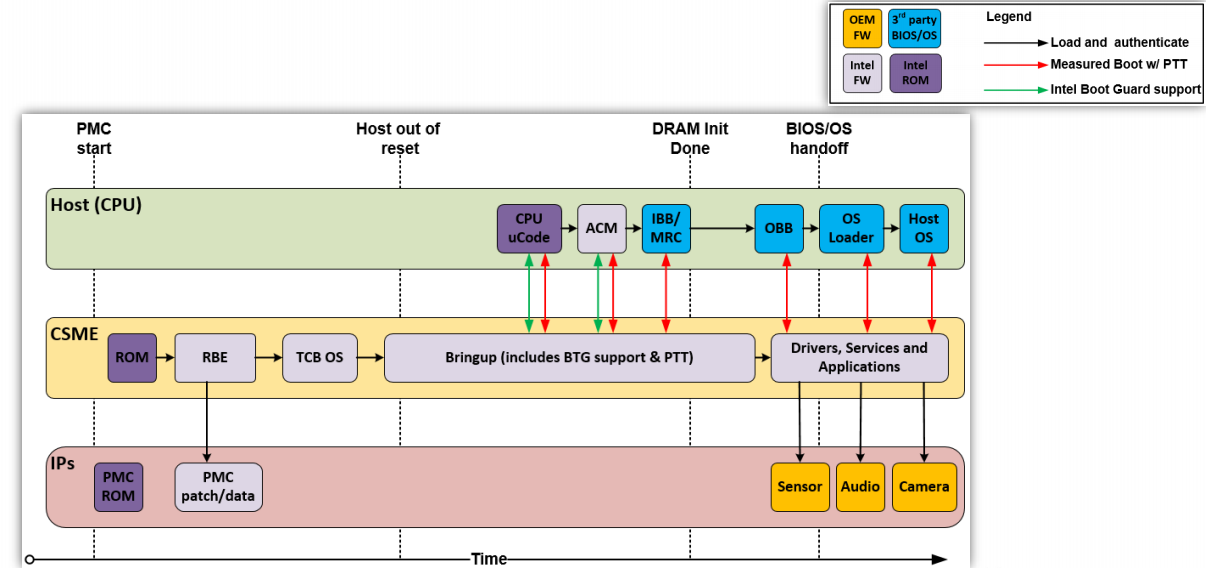
In addition to the three modules seen and described above, CSME has three main roles that define various system characteristics:
- Chassis
– Safe start of the platform
– Overclocking
– Loading of the microcode in the PCH and CPU HW motors - Security
– Isolated and reliable execution of security services (TPM, DRM and DAL) - Manageability
– Platform management in an out-of-band network (AMT)
These three roles are determined and directly dependent on others that complete each platform, such as ISA or AT for security, but basically define what CSME can or cannot do within each module.
As expected, attacks have been more and more frequent to this engine engine, since breaking through it gives the attacker a very clear advantage to take control of the system to the point of being able to work directly from BIOS / UEFI, being able to load malicious microcodes on the CPU.
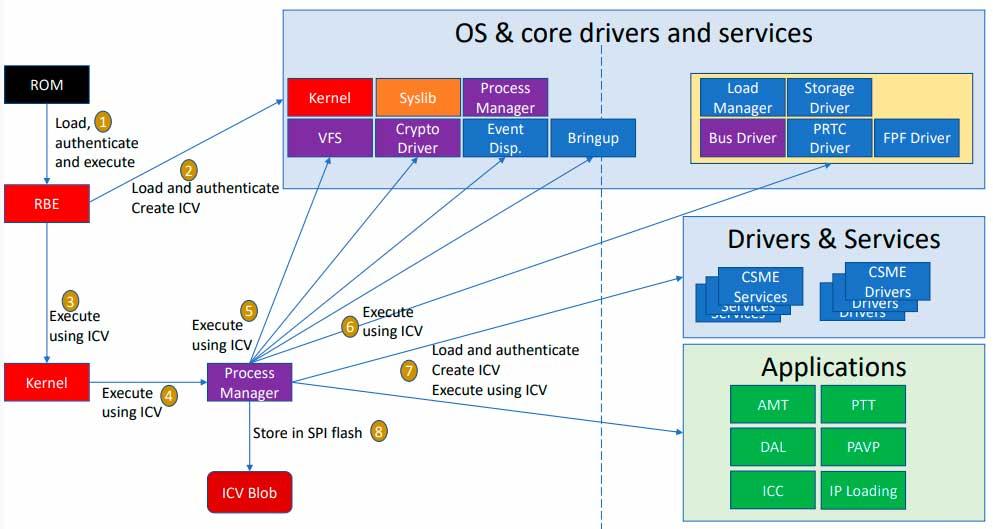
For this reason, Intel is very careful when offering information about the management of the entire system, since it is capable of controlling SRAM, ROM, SYSTEM Agent, OCS or Gaskets, for example.
Therefore, and although Intel does update the three main modules using firmware, it is highly recommended to search the Internet for the latest versions of them and install them, always keeping the latest UEFI available, where we will not only correct errors or improve compatibility, but that we will always keep security to the maximum.