When you embark on the journey of purchasing an SSD, your aim is typically to find a unit that offers the best performance relative to its price. One of the key metrics you’ll consider is sequential speed. However, there’s another speed metric known as random speed. Let’s delve into the differences between these two.
SSDs, like any other computer component, come with an array of specifications and pertinent details. Firstly, you’ll scrutinize the format it follows, followed by the type of interface it utilizes. These two attributes are typically the first ones you’ll assess.
Following that, your attention naturally shifts to the reading and writing speeds, typically measured in MB/s. Yet, it’s important to note that within these specifications, there are two distinct types of speeds: sequential and random. While sequential speed often takes the spotlight, both of these metrics hold significant importance, and it’s essential to comprehend their distinctions.

What is the speed of an SSD
When we talk about the speed of an SSD, we’re essentially referring to the rate at which data can be both read from and written to the drive in a single second. Typically, the reading speed tends to be higher than the writing speed. The reason for this disparity lies in the fact that the writing process generally requires a bit more time, resulting in a reduced volume of data that can be written in a second.
Within the realm of SSDs (and HDDs as well), we encounter two fundamental speed categories: sequential and random. While their names offer a hint regarding what they measure, let’s take a closer look at these two concepts.
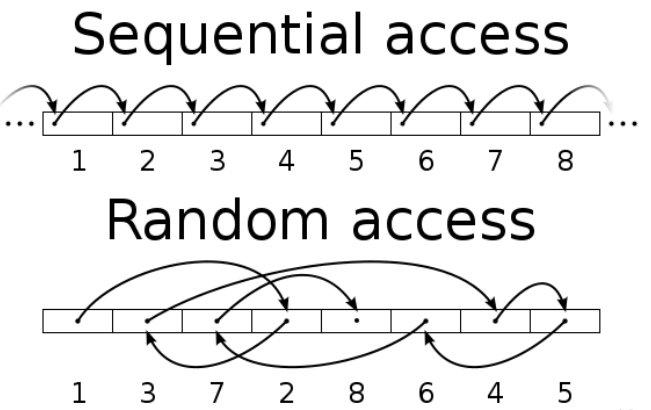
Sequential Speed:
When evaluating the performance of an SSD, sequential speed is often the primary benchmark used to determine whether a unit is fast or slow. It measures the amount of data that can be read from or written to the SSD in a continuous, linear manner.
- Sequential Read Speed: This metric gauges the SSD’s ability to read data that is stored sequentially. Think of it like reading a book, where you progress through the pages one after the other.
- Sequential Write Speed: This parameter signifies the SSD’s capacity to write new data in a continuous, sequential manner, akin to writing on a sheet of paper.
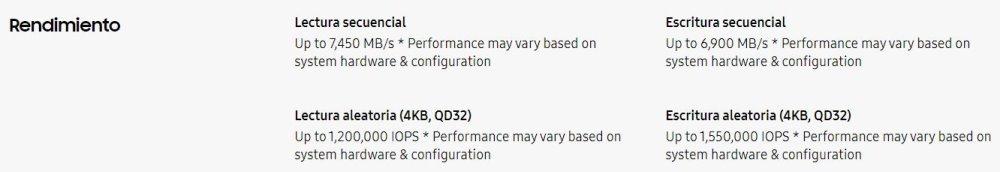
Both of these speeds are typically measured in Megabytes per second (MB/s), where higher values indicate the SSD’s ability to read and/or write more data per second.
Random speed
However, data access and writing are not always sequential; in fact, it’s often the opposite. Computers frequently read and write data in a random manner because data is scattered across various locations within the storage medium.
- Random speed comes into play in such scenarios. It measures how quickly data can be accessed or written randomly rather than sequentially. This is particularly evident during system startup when the computer needs to access various files, drivers, and utilities scattered across the storage medium.
Random speed is quantified in Input/Output Operations Per Second (IOPS), where higher IOPS values indicate better random data access and writing performance.
Interestingly, random write speeds are usually higher than random read speeds, in contrast to sequential speed, where reading is typically faster than writing.
Which is more important?
Both sequential and random speeds are important, and they are often closely related. If an SSD has a certain sequential read speed, its random read speed will be similar or nearly identical.
However, sequential speed tends to receive more attention, mainly because it is easier for users to understand, given that it is expressed in MB/s, a more user-friendly unit of measurement. IOPS, on the other hand, is a bit more abstract.
In conclusion, both parameters are interrelated, and a focus on sequential speed is often sufficient for most users.