Since the launch of Windows 10 we have seen how Redmond has not stopped working on improving what until now for the majority of users of the Microsoft system is the best version. Before each new version or compilation from the company, the news that each one of them will bring is usually announced, however, there are times when the company includes certain features or functions without mentioning anything about it. This is the case of the Windows 10 sniffer , a utility available in the system since the October 2018 update and that few users have discovered and used.
The truth is that it is not about any adjustment or configuration that allows us to personalize any aspect of our desktop, but it is a very useful tool for those who want to control certain activity or determine the cause of the latency of their connection.
What is Windows 10 sniffer
It is a specific function to control or monitor the propagation of data packets , which can help us to detect certain problems or an increase in the latency of our network, identify the applications affected, etc.
Since its integration, there are sure to be many users who have looked for a third-party sniffer to control or track traffic on their network without knowing that the system itself had its own sniffer. These packet trackers are diagnostic tools that allow you to analyze the network and detect or diagnose network problems.
In this case, the Windows 10 sniffer is a command-line based tool and has been named Packet Monitor. Its executable is located in the Windows System32 folder , therefore, it means that we can launch said tool at the command prompt or Windows PowerShell.
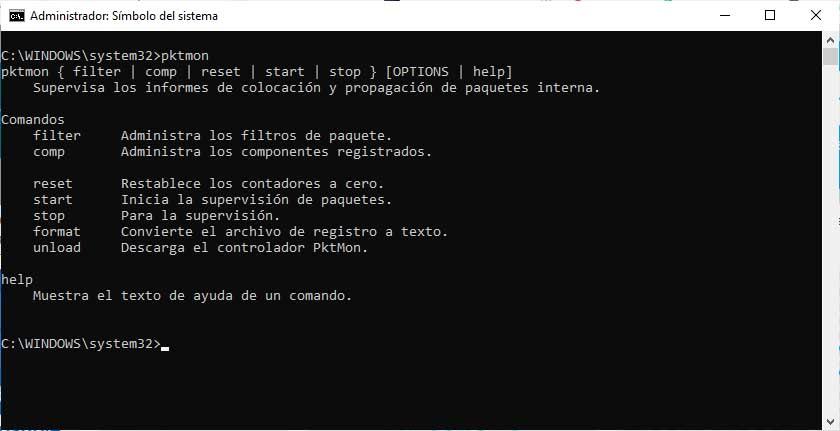
How to use the PktMon.exe sniffer
To use Packet Monitor the first thing we have to do is open a command prompt window or Windows PowerShell with administrator permissions. Once in front of the command line, if we type pktMon and press Enter we will find that the command syntax and the possible commands to use will be shown.
The correct PktMon syntax is:
pktmon {filter | comp | reset | start | stop} [OPTIONS | help]
Being the commands:
- filter Manages packet filters.
- comp Manages registered components.
- reset Reset the counters to zero.
- start Starts monitoring of packages.
- stop For monitoring.
- format Converts the log file to text.
- unload Download the PktMon driver.
If we need to get more help about a specific command, then we can use the following command:
Pktmon command help . For example, Pktmon filter help.
As soon as this instruction is executed, we will be shown information about the syntax and the possible commands to use for pktmon filter or the indicated command. These are the syntax and commands available for each case:
pktmon filter {list | add | remove} [OPTIONS | help]
Commands:
- list: Shows the active packet filters.
- add: Adds a filter to control which packages are reported.
- remove: Remove all filters.
pktmon comp {list | counters} [OPTIONS | help]
Commands:
- list: Lists all active components.
- counters: Shows the current counters by component.
pktmon reset [-counters]
Reset all component counters to zero.
pktmon start [-c {all | nics | [ids …]}] [-d] [–etw [-p size] [-k keywords]] [-f] [-s] [-r] [-m]
Starts packet monitoring.
- -c, –components: Select the components to monitor. They can be all components, only NIC, or an id list. of components. The default is all.
-d, –drop-only: Only report dropped packages. By default, correct packet propagation is also reported. - ETW registration
- –Etw: Starts a registration session for packet capture.
- -p, –packet-size: Number of bytes to be registered from each packet. To always log the entire packet, set the value to 0. The default value is 128 bytes.
- -k, –keywords: Hexadecimal bitmask (that is, the sum of the following marks) that controls which events are logged. By default, all events are logged.
- -f, –file-name: .etl log file. The default value is PktMon.etl.
- -s, –file-size: Maximum size of the log file in megabytes. The default value is 512 MB.
- Registration mode
- -r, –circular: New events overwrite the oldest when the maximum file size is reached.
- -m, –multi-file: A new file is created when the maximum file size is reached.
pktmon stop
Stops monitoring packages and displays the results.
pktmon format log.etl [-o log.txt]
Converts the log file to text format.
pktmon unload
Stops the PktMon driver service and downloads PktMon.sys. Equivalent to ‘sc.exe stop PktMon’.