We all know that PCs have a BIOS , that famous blue screen with yellow letters that serves to configure some parameters of the PC, but do you know what it is exactly? In this article we are going to tell you what the BIOS is, what is its definition , its characteristics and what exactly are its functions .
The BIOS is a “concept” that is frequently named in the computer world, and although almost everyone has a vague concept of what it is and what it is for, few are those who know it exactly. So, next we are going to explain everything to you so that you can fully understand the concept.
What is BIOS?
BIOS stands for ” Basic Input Output System “, which means something like “Basic input and output system”. It is firmware installed on a ROM (non-volatile) memory of the computer, often on a dedicated chip. It is a fundamental element in booting a PC because it is the bridge between the hardware and the software of the system: essentially, it is what explains to the software how the hardware should work.

Note: BIOS is pronounced as is in Spanish, but is pronounced “by-os” in English. Not to be confused with other acronyms such as “Basic Integrated Operating System” or “Built-in Operating System”.
What is the BIOS for on a PC?
The BIOS takes care of very low-level functions on the PC, such as the boot sequence (what storage device the operating system is on and how to boot from it) or how to operate the keyboard.
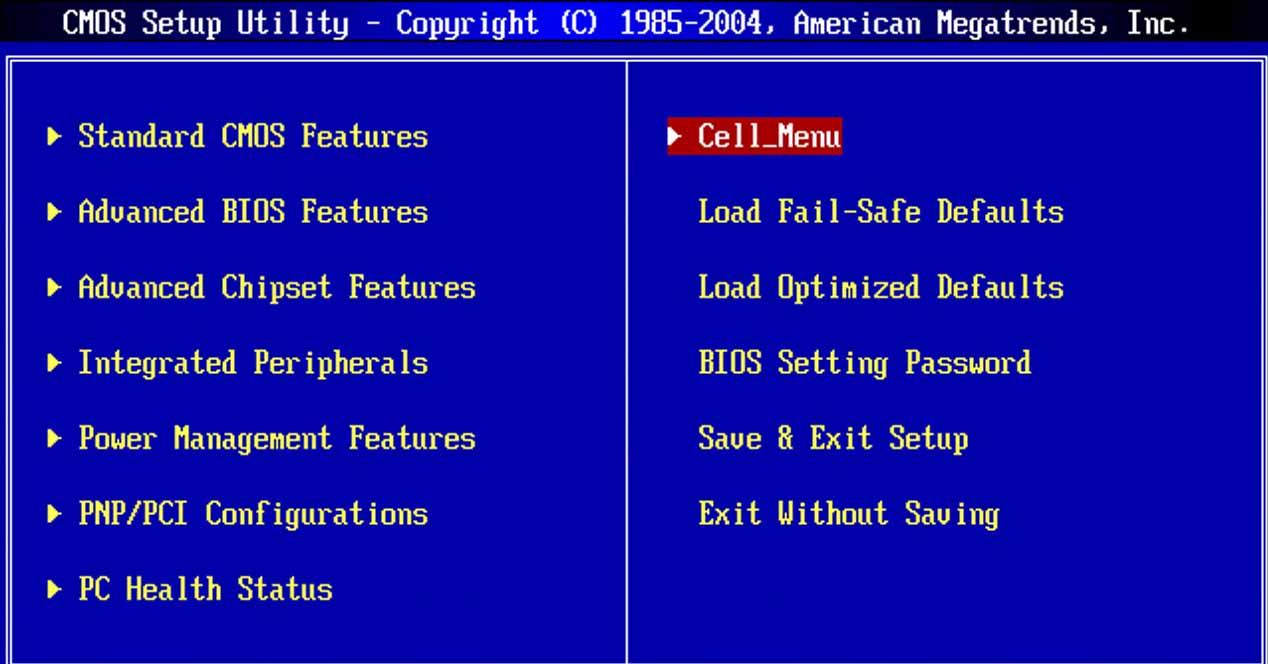
It also serves to identify and configure hardware components such as hard drives, external storage devices, the processor or RAM, and it is in fact from the BIOS where we can modify, for example, the operating parameters of the processor to deactivate cores, activate and disable HyperThreading / SMT, or modify its speed to Overclock or Underclock.
Main BIOS functions on a PC
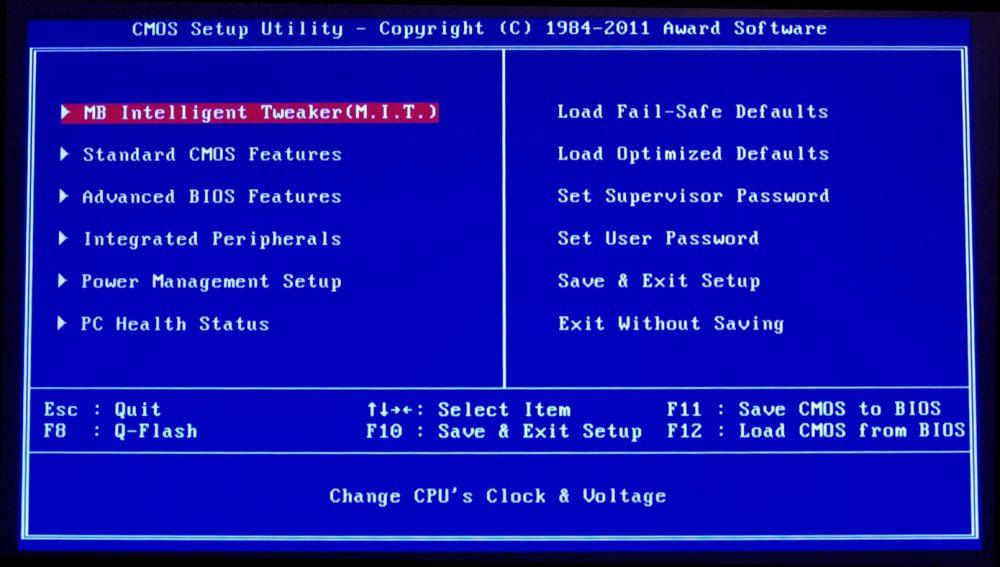
In the BIOS of a PC we can modify an enormous amount of hardware configuration options. As a general rule you will only have to enter the BIOS, change the parameter, save the changes and restart the PC for them to take effect, since as we have mentioned before the BIOS affects the PC’s boot system and is the first thing that the hardware consults to know how it has to behave.
These are the main functions that you can modify:
- Change the order of the boot sequence.
- Load factory settings.
- Update the BIOS.
- Create / change / disable the access password.
- Change the computer date and time.
- Change the settings of the storage units.
- Change disk / optical drive settings.
- View the amount of memory installed in the system.
- Configure whether we want the numeric pad of the keyboard to be active or not.
- Enable or disable the motherboard manufacturer’s logo at startup.
- Activate or deactivate POST (Power On Self Test).
- Enable or disable the internal cache of the processor.
- Change processor options and behavior.
- Change options and speed of RAM.
- Change the voltages.
- Create RAID systems from storage devices.
- Enable or disable IEE1394.
- Enable or disable the on-board sound card.
- Enable or disable RS232 / LPT ports.
- Enable or disable ACPI.
- Change the behavior of the PC power button.
- Change boot options.
- Enable or disable multiple monitors on startup.
- Change the behavior of PWM fans.
- Monitor PC temperatures.
How do you access to enter to configure the PC parameters?
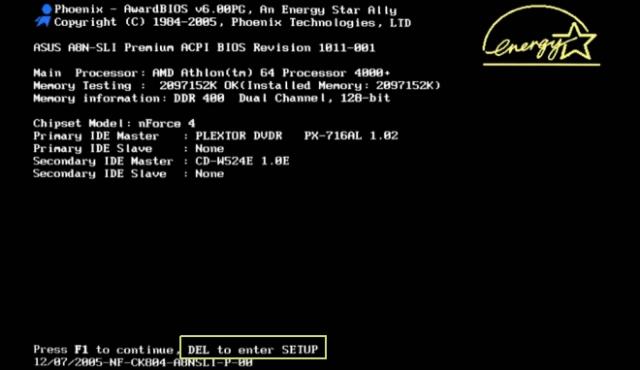
As a general rule, as soon as we press the power button on the PC we can access it by repeatedly pressing the DELETE key on the keyboard, although on some computers this changes and the key is F2 (Insyde) or F1 (Microid). In many PCs we can also partially access specific BIOS functions, such as pressing F10 to simply select the storage device from which we want the system to boot.
Main manufacturers
Although the purpose is the same, there are several BIOS manufacturers that we can find, the main ones being: