While 3D printing is a familiar concept to many, 4D printing represents an exciting leap forward, harnessing the power of external energy inputs to transform 3D-printed objects into dynamic structures with incredible potential.
Let’s delve into how 4D printing works and explore its wide-ranging applications that could revolutionize various aspects of our lives.
Understanding 4D Printing
4D printing is a cutting-edge process that involves the transformation of 3D-printed objects into different shapes and functionalities when exposed to external energy inputs, such as temperature, light, or other environmental stimuli. To illustrate this concept, consider a simple example: imagine a material that responds to sunlight by actively reorienting itself to face the sun. By 3D printing a sunflower using this material, you’d create a 4D figure that mimics the behavior of a real sunflower, following the sun’s path throughout the day.
This basic example showcases the transformative potential of 4D printing, which extends far beyond leisure and entertainment into fields like healthcare, national security, education, and more.
Materials Used in 4D Printing
Numerous materials are employed in 4D printing, and ongoing research promises even greater possibilities in the future. Some of the materials currently in use include:
- Shape Memory Polymers (SMP): These materials can return to a predetermined shape when exposed to a specific stimulus, such as heat.
- Liquid Crystal Elastomers (LCE): LCEs contain heat-sensitive liquid crystals, causing them to change shape when subjected to temperature variations.
- Hydrogels: Composed primarily of water, hydrogels are known for their biocompatibility and find applications in the medical field.

Applications of 4D Printing
The applications of 4D printing are diverse and promising, with countless possibilities on the horizon. Here are a few examples:
- Medicine: 4D-printed medical devices could adapt to the body’s needs, such as stents that change shape according to vessel size.
- National Security: Transformative materials could be used for camouflage that adapts to various environments, enhancing stealth.
- Education: Dynamic models and teaching aids can help students better understand complex concepts by visually demonstrating changes in shape and behavior.
- Fashion: 4D-printed clothing might adjust to changing weather conditions, eliminating the need to plan for unexpected rain or temperature shifts.
- Manufacturing: Objects could self-assemble or adapt to fit different components, simplifying production processes.
- Consumer Electronics: Adaptive materials could lead to devices that reshape themselves to optimize comfort and functionality for users.
4D Printing in Action
To grasp the full potential of 4D printing, consider watching videos that showcase real-world examples. These videos demonstrate how objects can seamlessly transform, such as a car adapting to a driver’s body or clothing that adjusts to weather conditions.
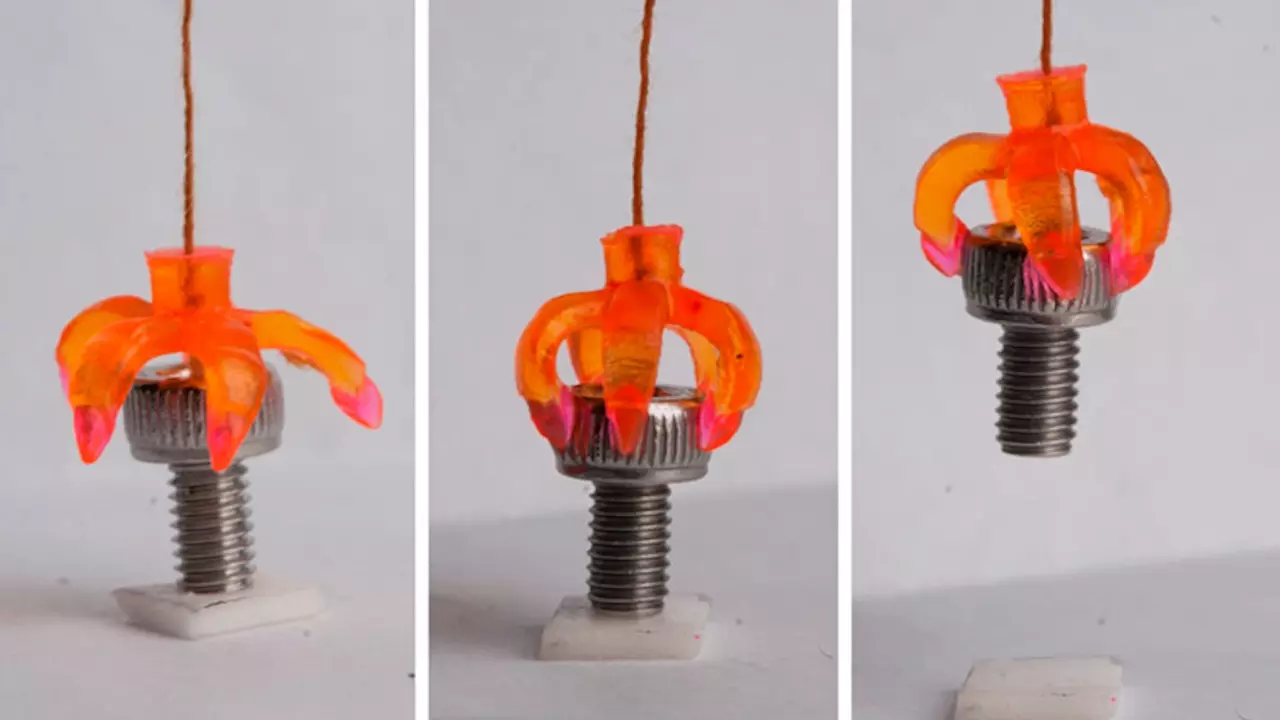
Intriguingly, 4D printing can enable objects to respond to their surroundings without external force. Imagine the pieces of a mobile phone self-assembling in a mixing chamber to create a fully functional smartphone.
The captivating cover image of this article depicts an object that autonomously closes its “arms” to grasp another object upon contact. This behavior occurs solely due to the composition of its material, which reacts to the material it encounters.
While we’ve provided a brief overview of how 4D printing works and its potential applications, there is much more to explore in this fascinating field. If you’re intrigued by 4D printing, we encourage you to delve deeper into the subject, as you’re sure to uncover more astonishing innovations and possibilities.