As you know, a microphone is a device that is responsible for transforming sound waves into electrical impulses, transforming an analog signal into a digital one. To carry out this process, the microphones use different formats and with different types of components, each one with its peculiarities, advantages and disadvantages, so in this article we are going to summarize all the types of microphones out there to see which one is the best result. It will give you according to your needs.
Although the purpose is the same regardless of the type of microphone used, not all use the same method to transform sound waves into electrical signals, and depending on the way in which the sound is processed, one result or another is obtained.

Microphone types according to their construction
We will start by looking at the types of microphone that exist according to how they have been manufactured, that is, according to how they manage to transform the sound waves of our voice into electrical impulses that can be interpreted by a sound card, such as the PC.
Dynamic microphones
This type of microphone is the most common and used today, since it does not need any type of electrical supply to work: they simply connect to the audio equipment and work without the need for anything else. The frequency response and sensitivity value is quite acceptable despite the fact that they are also the simplest in construction, so they are also the cheapest.
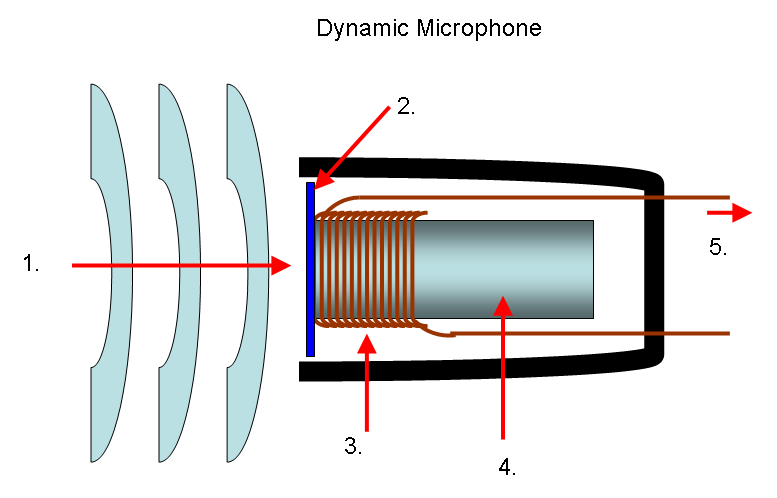
Its way of working is based on the principle of electromagnetism, by which if we place a wire around the magnet we create a coil; When moving within the magnetic field an electric current is generated, so you only have to add a membrane so that it moves through the sound waves that reach the microphone, and as the membrane is connected to the coil, it generates the electrical impulses .
Condenser microphones
A capacitor is an electrical component capable of storing energy whenever electricity is applied to it. These types of microphones have two plates, a rear one that is fixed and the other, the diaphragm, moves according to the pressure exerted by the sound waves that are applied to it. By varying the width between the two plates that make up the capacitor, current variations occur that are transmitted to the cable.
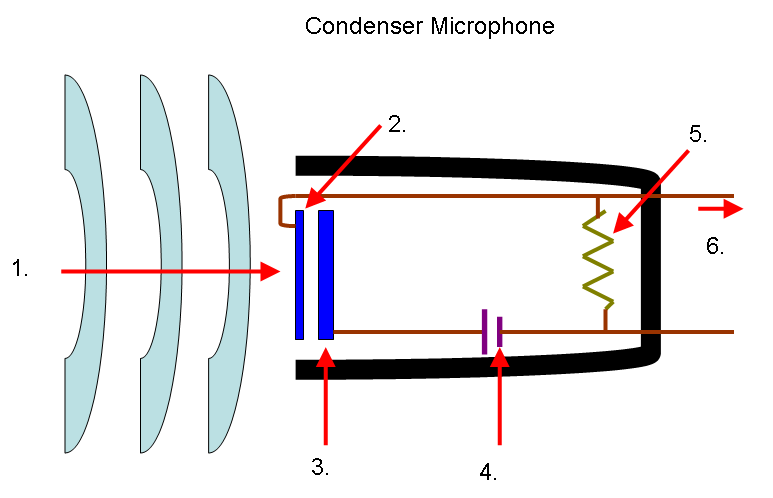
This type of microphone therefore needs power, known in this niche as phantom power to function. Although the cable is the same as that used in dynamic microphones, they have to be connected to a special console (known as a preamp) to have this type of power, which is generally + 48V.
These microphones are much more sensitive than the dynamic ones and therefore are the ones that are usually used in the professional field, but as always the good thing costs more money, since they are much more complicated to manufacture and therefore much more expensive.
Electrec, carbon, crystal and ribbon
Around 85% of the microphones on the market are dynamic or condenser, and the remaining 15% are made up of the other types of microphones that we are going to see below.
- Electrec: they are very similar to those of condenser but they do not need power since they integrate it in themselves. The diaphragm is a sheet that is factory charged with electrical energy (it is polarized), called precisely “Electrec”. Many PC microphones use this format.
- Of coal: small granules of coal are placed in an electrical circuit. Sound waves vary the resistance of the carbon, allowing electricity to flow. They are quite insensitive and of low fidelity and quality, but in return they are very resistant and cheap to manufacture, so they are often used in equipment designed for outdoor or in old phones.
- Glass: they take advantage of the characteristic of glass (generally quartz) to generate an electrical voltage when its sheets are deformed when receiving pressure from sound waves (this property is called the piezoelectric effect, such as the “speaker” of PCs). The problem with this type of microphone is that its properties change according to temperature and they have a fairly high manufacturing cost.
- Tape – A thin metal tape is attached to a magnet. The vibrations generated by the sound waves make the tape vibrate and being in a magnetic field, it generates the electrical signal. They are very delicate and expensive to manufacture but of the highest quality, so they are often used for recordings of musical instruments such as flutes, violins or clarinets.

Microphone types according to their format
Regardless of their construction, all microphones can have different formats that we can summarize in the following:
- Hand-held : they are the ones that are used regularly, since they can be used by holding them in the hand (as in interviews or live concerts) or placed on pedestals. Generally, condenser microphones already come with special supports to be placed on pedestals, with rubber bands (“spider”) that serve as suspensors to prevent the vibrations of the pedestal from entering the recording.
- Lapel or “Lavalier” : formerly they were placed on the tie or lapel of the announcer’s shirt. Now the models are more discreet and can be easily hooked onto any piece of clothing to hide them, so they are very small.
- Internal : we do not see them but they are there. They are the ones that are usually integrated into telephones, recorders or webcams.
- Headband : these are the ones we frequently see in gaming headphones that have the integrated microphone.
- Digital USB : they are currently taking over the market due to their versatility. The output of these microphones is digital thanks to the USB port, so they have the peculiarity that they do not even need a sound card since they themselves transform the signal from analog to digital. One option in this regard is to use XLR to USB adapters, something that many streamers do to use professional microphones without having to incorporate an expensive pre-set into their audio setup.