There’s been a lot of talk lately about Intel processors and the vulnerabilities that are affecting them. To correct these vulnerabilities and avoid existing ones, there is a mechanism called Intel CSE , and in this article we are going to tell you what it is, how it works and why it is so important in brand processors.
There are many vulnerabilities that can affect our computers, and one of the main sources for them is PC processors. For this reason, and in an attempt to minimize, alleviate, and nullify these problems, Intel created a security environment called TEE, of which Intel CSE is a part. Let’s see what it consists of.

What is Intel CSE?
Intel CSE is the abbreviation for Converged Security Engine , a mechanism that is integrated into the TEE ( Trusted Execution Environment ) and that globally consists of a set of firmware and hardware that provides a secure environment when executing any type of application, preventing the execution of malicious software that could damage the equipment or data leaks.

The TEE offers a secure way to run authorized security software and firmware known as Trusted Applications (TA), which can be developed in Java and implemented in the firmware. Within the TEE, each TA is independent from the others, and all of them must go through the CSE mechanism to verify their authenticity. The TEE also enforces the rights of protection, confidentiality, integrity and access to the resources and data to which those TAs belong.
In other words, for a software to be able to run on the computer, it must be in a kind of “white list” of applications that are reliable and verified as harmless to the system, and the Intel CSE mechanism is an important part of verifying this.
Security Certificates and the Importance of Intel CSE
One of the functions of the Intel CSE mechanism is the review of security certificates. For example, when we want to install a driver for a hardware component, it must be accompanied by a certificate that guarantees the authenticity of the data to be installed on the system.
You can see this for yourself in Windows, from the Device Manager you look for any component, access its properties and in the “Driver” tab, the “Driver details” button will show you this information.
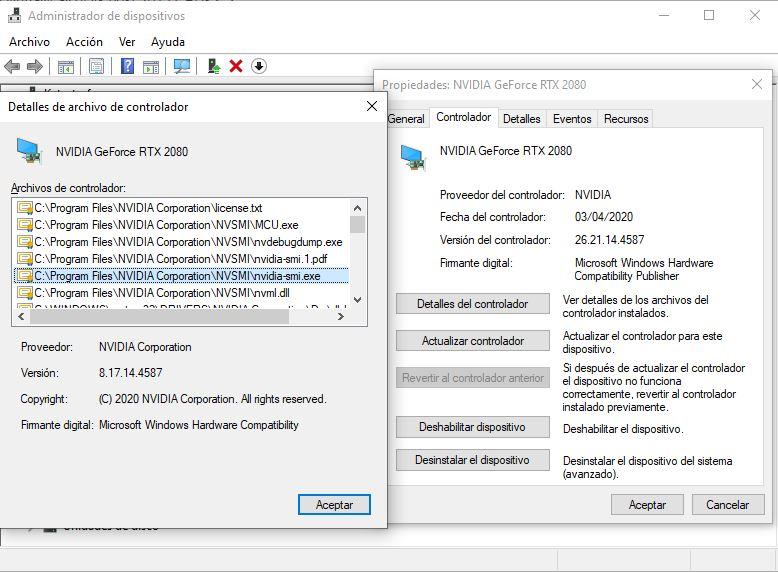
Each driver file installed on the system must be accompanied by its corresponding digital certificate, signed by the company (in the example we are seeing the properties of the graphic driver, signed by NVIDIA). The Intel CSE mechanism is in charge of verifying the veracity of these certificates to allow the execution of their code.
The “rings” of Intel privileges
Although some software is authorized at firmware level to perform certain tasks on the computer, it does not mean that you are given carte blanche to do what you want. To do this, Intel’s protection mechanism includes different levels of ring-shaped privileges through the Intel Management Engine .
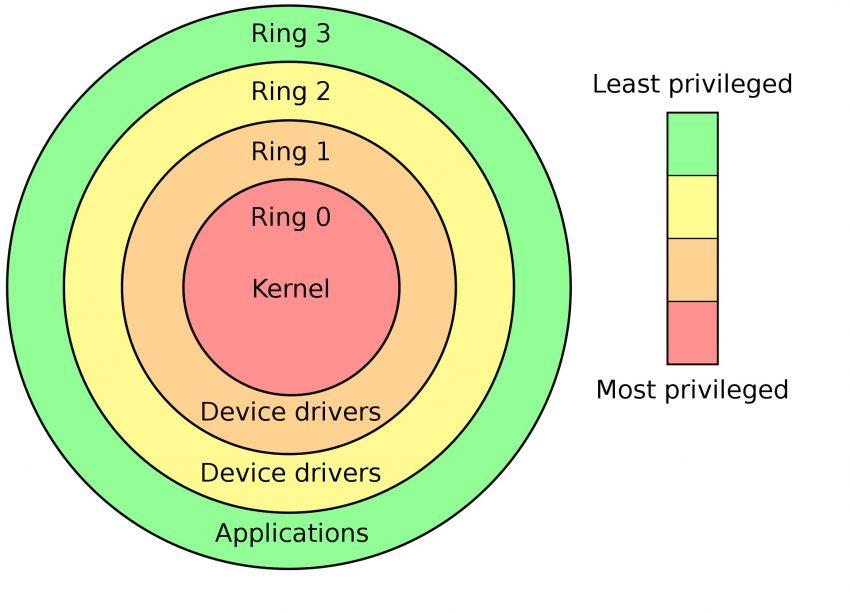
Colloquially, these categories are defined as follows:
- Ring 0: the highest privilege, which has access to the system kernel.
- Ring 1: allows access to the hypervisor, which can do remote actions.
- Ring 2: called “System Management Mode”, at this level you would find for example the drivers, which allow relative modifications in the execution code.
- Ring 3: Here you will find most applications, which simply use the processor’s instructions.