Docker is the cross-platform opensource project that automates the deployment of applications within containers using resource isolation features so you don’t have to use multiple resource-consuming virtual machines to accomplish the same task, reducing overhead and increasing scalability and portability.
In a short time, Docker has become the main application for container management worldwide and combined with other services such as Kubernetes, it has capabilities that cover almost all requirements, for all, except for some specific cases that we will discuss further in detail, since Docker is not suitable for all uses due to its design.

To start, a little history
The idea of Docker was born from the hand of Solomon Hykes as an internal project within dotCloud (founded in 2010), which was a company focused on creating a PaaS, it would be renamed Docker Inc., which is the current company that develops Docker Hub and Docker for desktop.
In its beginnings it used LXC as an execution environment that was later replaced by its own library written in the Go programming language called libcontainer to convert it into a multiplatform program.
What is Docker and what is it used for?

Its function coincides with the slogan and it is to develop, send and execute any application in any operating system, being a flexible alternative with a much less need for resources than traditional VMs that are emulations of hardware components based on virtual machines.
It is a container-based virtualization technology that shares the host kernel to run isolated processes in user space without the need to have another operating system running, consuming unnecessary resources.
Differences with traditional virtual machines
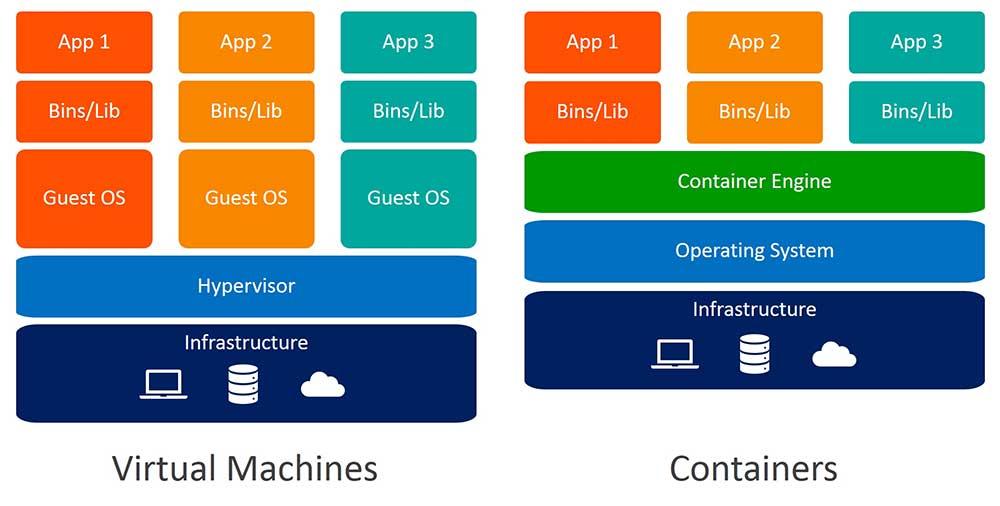
We will save all the resources used by virtualized operating systems and we can also run our containers on any operating system where Docker is installed in order to run our applications.
Keep in mind that Docker is not valid for all types of applications because it is intended for micro-services without graphical user interfaces, so it is not always the best option compared to the use of virtual machines because perhaps we do want to use a graphical interface and then the use of a virtual machine would be a better option. In addition, the persistence of Docker is non-existent, so if we turn off any of the containers, all the information contained in it will disappear, so for this type of service it is better to use a separate service or use a virtual machine for this purpose.
What makes up Docker?
It is made up of three fundamental components that are the Docker engine, the Docker images and the Docker Hub.
The Docker engine is a client-server application with 3 fundamental components:
- The Docker Daemon (server) which is the process that runs in the background on the host and is responsible for creating and managing the images, containers and network processes.
- The REST API is a REST- based programming interface that is responsible for interacting and giving instructions to the daemon.
- The terminal (client) is in charge of providing the interface to interact with the daemon through the REST API with scripts or commands.
Docker images are the containers that the user creates or downloads from the Docker Hub and contain the resources necessary to run a specific application and the application to be executed.
The Docker Hub provides Docker images to make it easy for users to download containers with pre-made services saving a lot of time. It is an online library with many public repositories where you will find everything you need to get started, although it also has private repositories.
What advantages does it have?
The most important thing is in the scalability since the containers are easily replicable and thus provide high availability , since if one fails, there will still be other containers offering the service. In addition, it can be used in all operating systems that have the Docker platform installed, so it offers excellent portability , since it can be created in an Ubuntu Focal Fossa, for example, and then bring that service to a Windows Server and it works at perfection as on the machine where it was created.
The great advantage is that applications with different requirements can be run in isolation using basic Linux Kernel functions that are Cgroups and Namespaces.
Cgroups limit the access of processes to the use of memory, CPU and input and output, preventing different processes from eating resources from other processes.
Namespaces limit processes and threads by encapsulating them, using 5 specific fields:
- UTS or systems identifier are used to assign the containers the domain and computer name.
- PID or process identifier is used in each Docker container with a separate namespace so that all processes outside the container are not affected if they have the same PID avoiding conflicts because they are encapsulated.
- IPC or communicator between processes is responsible for isolating the processes in each container, avoiding communication with external processes.
- NET or network resources is responsible for assigning to each container the network resources it needs to have connectivity.
- MNT or file system mount point is responsible for isolating the reserved space of the container so that it is only accessible from the Docker container
As we mentioned before, in its beginnings Docker used LXC, which was later replaced by libcontainer, which allows Docker to become cross-platform, being able to run on both Linux and Windows, as well as MacOS because if it continued to use LXC, it would only be able to run on Linux environments.
What disadvantages does it have?
It has 5 main disadvantages to take into account when we decide to use Docker for the virtualization of applications in containers:
The execution speed is not the same as if we run the application directly on the host . Containers, while greatly reducing overhead compared to using a virtualized operating system, running the same application does not come at the same speed as if it were running directly on the host.
The container ecosystem is fractured and some of the containers do not work with others such as Red Hat OpenShift that only works with Kubernetes.
Using Docker for persistent storage should not be an option , because because of the way it has been designed once a container disappears, all its contents also disappear so all persistent storage as from a database should never be in a Docker container, since we are at risk of information loss.
Applications with graphical interfaces do not work well because Docker by design does not require a graphical interface, since it is oriented towards server applications.
Not all applications benefit from the use of containers because they are mainly intended for micro-services.
Difficulty
With the desire to learn, the difficulty is slightly greater than non-container based virtualization, since it does not have a graphical user interface like those offered by virtualization solutions for operating systems such as QEMU, HyperV, VMWare or VirtualBox It becomes perhaps a little more difficult at first. But as we have already discussed, these non-container based virtualization techniques have a much lower overhead providing a great advantage over SO virtualization and there are many tutorials and videos available on the Internet on YTube to learn about Docker in no time with little effort.
Download
We will have the possibility to download Docker for free from the developer’s website and we will also have access to a lot of documentation that provides us with how it is used.